VNC: Difference between revisions
(Some sort of strange end-of-line pre mode trigger that went away when I retyped the text) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (313 intermediate revisions by 15 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages /> | |||
<translate> | |||
<!--T:1--> | |||
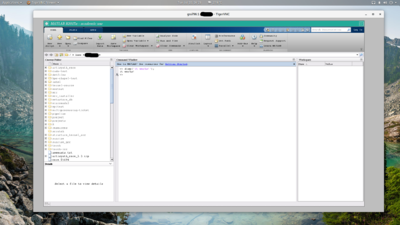
[[File:Matlab-vnc.png|400px|thumb|MATLAB running via VNC.]] | |||
<!--T:2--> | |||
It is often necessary to remotely start the graphical user interface for complex software packages such as [[MATLAB]]. The most common way to do this is with [[SSH]] and X11 forwarding. However the performance of SSH+X11 is often too slow similar to [https://docs.computecanada.ca/wiki/Connecting_with_MobaXTerm MobaXTerm] or [https://docs.computecanada.ca/wiki/Connecting_with_PuTTY Putty]. A much better alternative is to use [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_Network_Computing VNC] to connect to a remote desktop. | |||
= Setup = <!--T:4--> | |||
<!--T:6--> | |||
First you will need to install a VNC client on your machine to connect to the VNC server. We recommend using [http://tigervnc.org/ TigerVNC]. A TigerVNC package is available for Windows, MacOS and most Linux distributions. The following shows how to download, install and configure TigerVNC securely for each operating system. The certificate configuration steps are only required for connecting to VDI nodes so the signing authority of the certificate presented by the vncserver is known. If a popup about a certificate issue occurs, either you have not configured it properly or you are not connected to our server and should not enter your password. | |||
== Windows == <!--T:8--> | |||
<!--T:10--> | |||
Download and run the latest stable vncviewer64-x.y.z.exe version package installer from [https://sourceforge.net/projects/tigervnc/files/stable/ the official download page] ( for example <code>vncviewer64-1.12.0.exe</code>). Make sure you download the viewer and not the server. To create secure tunnels from your desktop to the vncserver as described in the sections below, you will need to open a terminal window and run the SSH command. This may be done using PowerShell standard on Windows 10 since the 1809 update. | |||
== MacOS == <!--T:12--> | |||
<!--T:14--> | |||
Install the latest stable DMG package by going to [https://sourceforge.net/projects/tigervnc/files/stable/ the official download page] and click the green <b>Download Latest Version</b> button for <code>TigerVNC-1.12.90.dmg</code> (as of January 2023). Once the download is complete double click the DMG file to open it. A TigerVNC Viewer icon should appear in a popup window along with a LICENSE.TXT and README.rst file. To complete the installation, drag the tigervnc icon that appears into the Applications folder and/or the lower [https://support.apple.com/en-ca/guide/mac-help/mh35859/mac app dock]. To remove the popup you will need to unmount the DMG file. To do this open a New Finder Window, verify <code>View->ShowSidebar</code> is selected, click the small up arrow beside <code>TigerVNC-1.12.90</code> in the left side menu and lastly close the finder window. If you are running macOS Monterey 12.2 and [https://github.com/TigerVNC/tigervnc/issues/1423 TigerVNC crashes] then you must upgrade to this latest version. | |||
== Linux == <!--T:16--> | |||
== | |||
{ | <!--T:18--> | ||
|sudo apt-get install tigervnc-viewer | First install TigerVNC viewer with the package manager for your Linux version: | ||
| | |||
| | <!--T:20--> | ||
} | {| class="wikitable" | ||
== | ! Linux Version | ||
! Install Command | |||
|- | |||
| Debian, Ubuntu | |||
| <code>sudo apt-get install tigervnc-viewer</code> | |||
|- | |||
| Fedora, CentOS, or RHEL | |||
| <code>sudo yum install tigervnc</code> | |||
|- | |||
| Gentoo | |||
| <code>emerge -av net-misc/tigervnc</code> | |||
|} | |||
<!--T:22--> | |||
Next, start TigerVNC by either finding it in the applications menu or running <code>vncviewer</code> on the command line. In the "VNC Viewer: Connection Details" window that appears click "Options -> Security" then tick all boxes except "Encryption None" and enter one of the following paths in the "Path to X509 CA Certificate" field. | |||
<!--T:24--> | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! Linux Version | |||
! Path to X509 CA Certificate | |||
|- | |||
| Debian, Ubuntu | |||
| /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt | |||
|- | |||
| Fedora, CentOS, or RHEL | |||
| /etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt | |||
|- | |||
| Gentoo | |||
| /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt | |||
|} | |||
To save the settings click OK and then click Connect. If Connect is not clicked, the settings will not be saved. | |||
= Connect = <!--T:26--> | |||
<!--T:28--> | |||
Now you need a VNC server to connect to. This can be either a persistent vncserver running on dedicated VDI nodes which are part of [[Graham]], or a temporary vncserver you start on a cluster compute node. VNC is not a heavyweight server, so you can certainly run lightweight sessions on cluster login nodes. | |||
== VDI nodes == <!--T:30--> | |||
<!--T:32--> | |||
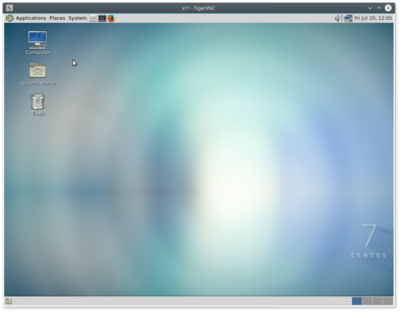
[[File:TigerVNC-GrahamDesktop.png|400px|thumb|right|'''gra-vdi.alliancecan.ca''']] | |||
<!--T:34--> | |||
Graham has two dedicated VDI (aka Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) nodes collectively known as gra-vdi. These nodes provide a remote desktop environment equipped with accelerated OpenGL. They are intended for the most demanding and complex interactive graphical tasks. The VDI nodes share Graham's <code>/home, /project,</code> and <code>/scratch</code> filesystems. As a result, any data files or directories created on graham by running jobs in the queue will immediately be accessible on gra-vdi for visualization and post-processing purposes without the need to transfer them over. | |||
<!--T:36--> | |||
To connect to gra-vdi, start VNC viewer (tigervnc) on your laptop and enter <code>VNC server: '''gra-vdi.alliancecan.ca'''</code>. This will bring up a login screen where you can enter your Alliance credentials. A desktop session will then be started on either gra-vdi3 or gra-vdi4 using a round robin algorithm. | |||
<!--T:179--> | |||
Users can also connect directly to either machine by specifying <code>VNC server: '''gra-vdi3.sharcnet.ca'''</code> or enter <code>VNC server: '''gra-vdi4.sharcnet.ca'''</code>. This may be useful if you find one machine is overloaded (oversubscribed) and thus not very responsive. Or if you consistently want to use the local $SCRATCH directory (defined as /local/tmp/$USER) on one server but not the other. Notice that $SCRATCH is defined differently on the clusters (as /scratch/$USER) where it is shared by all nodes. Similar to the clusters however, any data left on $SCRATCH on gra-vdi will eventually be deleted since the disc space is limited. Please do not plan to store any files on $SCRATCH for more than 60 days! | |||
<!--T:38--> | |||
Lastly, please keep in mind the VDI nodes are a shared resource and intended for visualization tasks. If you need to perform long-running computations within an application which uses a GUI (graphical user interface), then please log out of gra-vdi and instead connect to a compute node on any cluster as described in the <b>Compute Nodes</b> section below. This will ensure the memory and CPU resources on gra-vdi remain fully available for other users to conduct their own simultaneous graphical work without any noticeable performance impacts. | |||
== Login nodes == <!--T:41--> | |||
<!--T:42--> | |||
If you want to run a lightweight application in a remote VNC desktop (one that does not require much memory, cputime or a gpu since login node limits will apply here) you may start a VNC server on a cluster login node (such as graham) and then connect to it with the following procedure: | |||
<!--T:163--> | |||
[laptop:~] ssh graham.alliancecan.ca | |||
<!--T:44--> | |||
1) Since moving to [https://turbovnc.org turbovnc] on the clusters, the <code>-maxconnectiontime</code> vncserver option is no longer supported. Instead use <code>vncserver -idletimeout seconds</code> to ensure your session is eventually killed. This will ensure any unnecessarily consumed system resources associated with your desktop (such as memory) will be released. The first time you start vncserver you will be required to set a password which can be [https://docs.alliancecan.ca/wiki/VNC#Vncserver_password changed] later. The password will be required to remotely connect to your desktop with a vncclient (such as vncviewer). Likewise the password will be required when making [https://docs.alliancecan.ca/wiki/VNC#Multiple_connections multiple connections] assuming you started vncserver with the additional <code>-alwaysshared</code> option shown here (the square brackets mean optional and should not be included): | |||
[[ | <!--T:164--> | ||
[<b>gra-login2</b>:~] vncserver -idletimeout 604800 [-alwaysshared] | |||
Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? n | |||
Desktop 'TurboVNC: gra-login2:2 (username)' started on display gra-login2:2 | |||
Starting applications specified in /cvmfs/soft.computecanada.ca/gentoo/2023/x86-64-v3/usr/bin/xstartup.turbovnc | |||
Log file is /home/username/.vnc/gra-login2:2.log | |||
<!--T:175--> | |||
2) Determine the listening port (5903 in this example): | |||
<!--T:165--> | |||
[gra-login2:~] grep -iE "\sport|kill" /home/username/.vnc/gra-login2:2.log | |||
03/09/2024 17:48:40 Listening for VNC connections on TCP port 5903 | |||
<!--T:166--> | |||
[gra-login2:~] exit | |||
<!--T:46--> | |||
3) Open a terminal window on your desktop and start a SSH tunnel to the VNC server: | |||
<!--T:167--> | |||
[laptop:~] ssh graham.computecanada.ca -L 5901:<b>gra-login2</b>:5903 | |||
<!--T:48--> | |||
4) Open another terminal window on your desktop and connect with vncviewer: | |||
<!--T:169--> | |||
[laptop:~] vncviewer localhost:5901 | |||
<!--T:52--> | |||
Mac or Windows users should click the <i>TigerVNC Viewer</i> application icon on their desktop and enter the '''localhost:port''' information in the "Connection Details" dialogue box that appears. Keep in mind that strict memory and cputime limits apply on cluster login nodes. On Graham, these are 8GB and 1 cpu-hour per process according to <code>ulimit -t -v</code>. If you require more resources, then run your VNC server on the VDI nodes or compute nodes instead as described above and below respectively. | |||
== Compute nodes == <!--T:54--> | |||
<!--T:56--> | |||
Where VDI login nodes are unavailable you can start a VNC server on a compute node, and with suitable port forwarding, connect to it from your desktop. This gives you dedicated access to the server, but does not provide a full graphical desktop or hardware-accelerated OpenGL. | |||
<!--T:58--> | |||
<b>1) Start a VNC server</b> | |||
<!--T:60--> | |||
Before starting your VNC server, log in to a cluster (such as Cedar) and create an allocation on a compute node using the <code>salloc</code> command (a 24hr maximum time limit applies). For example, to request an [[Running_jobs#Interactive_jobs|interactive job]] using 4 CPUs and 16GB of memory you could use the command: | |||
<!--T:141--> | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
[username@cedar5:~/project] salloc --time=1:00:00 --cpus-per-task=4 --mem=16000 --account=def-username | |||
salloc: Pending job allocation 20067316 | |||
salloc: job 20067316 queued and waiting for resources | |||
salloc: job 20067316 has been allocated resources | |||
salloc: Granted job allocation 20067316 | |||
salloc: Waiting for resource configuration | |||
salloc: Nodes cdr768 are ready for job | |||
[username@cdr768:~/project] | |||
</source> | |||
<!--T:62--> | |||
Once your interactive job has started, one environment variable must be set in order to avoid some repetitive desktop errors: | |||
<!--T:142--> | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
[username@cdr768:~/project] export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=${SLURM_TMPDIR} | |||
</source> | |||
''' | <!--T:64--> | ||
Then, start a VNC server with <code>vncserver</code>. Take note of which node your job is running on. If unsure, you can use the <code>hostname</code> command to check. The first time you do this you will be prompted to set a password for your VNC server. '''DO NOT LEAVE THIS BLANK'''. You may change it later using the <code>vncpasswd</code> command. Continuing with the example: | |||
<!--T:143--> | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
[username@cdr768:~/project] vncserver | |||
You will require a password to access your desktops. | You will require a password to access your desktops. | ||
Password: | Password: | ||
Verify: | Verify: | ||
Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? n | Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? n | ||
xauth: file /home/username/.Xauthority does not exist | |||
New ' | New 'cdr768.int.cedar.computecanada.ca:1 (username)' desktop is cdr768.int.cedar.computecanada.ca:1 | ||
Creating default startup script /home/username/.vnc/xstartup | Creating default startup script /home/username/.vnc/xstartup | ||
Creating default config /home/username/.vnc/config | Creating default config /home/username/.vnc/config | ||
Starting applications specified in /home/username/.vnc/xstartup | Starting applications specified in /home/username/.vnc/xstartup | ||
Log file is /home/username/.vnc/ | Log file is /home/username/.vnc/cdr768.int.cedar.computecanada.ca:1.log | ||
</source> | |||
<!--T:66--> | |||
Determine which port the VNC server is using by examining the log file: | |||
< | <!--T:144--> | ||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
[username@cdr768:~/project] grep -iE "\sport|kill" /home/username/.vnc/cdr768.int.cedar.computecanada.ca:1.log | |||
vncext: Listening for VNC connections on all interface(s), port 5901 | vncext: Listening for VNC connections on all interface(s), port 5901 | ||
</ | </source> | ||
<!--T:68--> | |||
<b>2) Set up a SSH tunnel to the VNC server</b> | |||
<!--T:70--> | |||
Once your VNC server has been started, create a "bridge" to allow your local desktop computer to connect to the compute node directly. This bridge connection is created using an [[SSH tunnelling|SSH tunnel]]. SSH tunnels are created on your computer in a new local terminal window using the same SSH connection command as usual, with an extra option added which follows the format <code>ssh user@host -L port:compute_node:port</code>. | |||
An example SSH tunnel command to connect to a VNC server running on | <!--T:72--> | ||
An example of an SSH tunnel command run on your computer to connect to a VNC server running on Cedar's cdr768 node and port 5901 would be the following: | |||
<!--T:145--> | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
ssh username@ | [name@local_computer]$ ssh username@cedar.computecanada.ca -L 5902:cdr768:5901 | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
The SSH tunnel | <!--T:74--> | ||
The SSH tunnel operates like a normal SSH session: You may run commands over it, ''etc.'' However, keep in mind that this SSH session is also your connection to the VNC server. If you terminate the SSH session, your connection to the VNC server will be lost! For more information, please see [[SSH tunnelling]]. | |||
<!--T:76--> | |||
<b>3) Connect to the VNC server</b> | |||
<!--T:78--> | |||
If you have a Linux desktop, open a new local terminal window and tell your VNC client to connect to '''localhost:port'''. The following example uses the TigerVNC <code>vncviewer</code> command to connect to the running VNC server on cdr768. You will be prompted for the VNC password that you set up earlier in order to connect. | |||
<!--T:146--> | |||
{{Command | {{Command | ||
|vncviewer localhost | |vncviewer localhost:5902 | ||
|prompt=[name@local_computer]$ | |prompt=[name@local_computer]$ | ||
|result= | |result= | ||
| Line 153: | Line 219: | ||
See http://www.tigervnc.org for information on TigerVNC. | See http://www.tigervnc.org for information on TigerVNC. | ||
<!--T:147--> | |||
Tue Jul 10 17:40:24 2018 | Tue Jul 10 17:40:24 2018 | ||
DecodeManager: Detected 8 CPU core(s) | DecodeManager: Detected 8 CPU core(s) | ||
DecodeManager: Creating 4 decoder thread(s) | DecodeManager: Creating 4 decoder thread(s) | ||
CConn: connected to host localhost port | CConn: connected to host localhost port 5902 | ||
CConnection: Server supports RFB protocol version 3.8 | CConnection: Server supports RFB protocol version 3.8 | ||
CConnection: Using RFB protocol version 3.8 | CConnection: Using RFB protocol version 3.8 | ||
| Line 162: | Line 229: | ||
CVeNCrypt: Choosing security type TLSVnc (258) | CVeNCrypt: Choosing security type TLSVnc (258) | ||
<!--T:148--> | |||
Tue Jul 10 17:40:27 2018 | Tue Jul 10 17:40:27 2018 | ||
CConn: Using pixel format depth 24 (32bpp) little-endian rgb888 | CConn: Using pixel format depth 24 (32bpp) little-endian rgb888 | ||
CConn: Using Tight encoding | CConn: Using Tight encoding | ||
CConn: Enabling continuous updates | CConn: Enabling continuous updates | ||
}} | |||
<!--T:80--> | |||
If you are on a Mac or Windows desktop, click the <i>TigerVNC Viewer</i> application icon and enter the '''localhost:port''' information. For our example it becomes: [[File:VNCviewerConnect.png|400px|thumb'''Mac Tiger VNC Viewer Connection Details Dialogue Box''']] | |||
<!--T:82--> | |||
Please note the port number in '''localhost:port''' specified above (5902) must match the local port (the first number) you specified when you set up the SSH tunnel. The default VNC port is 5900. If you specified 5900 for the local port of the SSH tunnel, you could omit it when you invoke <code>vncviewer</code>. However, Windows users may find that they cannot set up an SSH tunnel on local port 5900. Once connected, you will be presented with a [https://mate-desktop.org/ Linux MATE desktop]. To launch a terminal, click on the top menu on "Applications -> System Tools -> MATE Terminal". You may also add a shortcut to the top menu by right-clicking on "MATE Terminal" and by clicking on "Add this launcher to panel". Finally, to launch a program, invoke the command as you would normally within a <code>bash</code> session, for example <code>xclock</code>. To start a more complicated program like MATLAB, load the module and then run the <code>matlab</code> command. | |||
= More information = <!--T:86--> | |||
== Vncserver password == <!--T:88--> | |||
<!--T:90--> | |||
To reset your VNC server password, use the <code>vncpasswd</code> command: | |||
<!--T:170--> | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
[gra-login1:~] vncpasswd | |||
Password: | |||
Verify: | |||
Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? n | |||
</source> | |||
<!--T:171--> | |||
Optionally you can completely remove your VNC configuration (including your password) by deleting your <code>~/.vnc</code> directory. The next time you run <code>vncserver</code> you will be prompted to set a new password. | |||
== Killing vncserver == <!--T:96--> | |||
<!--T:98--> | |||
If a vncserver is no longer needed, terminate it with <code>vncserver -kill :DISPLAY#</code> as shown here: | |||
<!--T:172--> | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
[gra-login1:~] vncserver -list | |||
<!--T:173--> | |||
TigerVNC server sessions: | |||
<!--T:174--> | |||
X DISPLAY# PROCESS ID | |||
:44 27644 | |||
<!--T:99--> | |||
[gra-login1:~] vncserver -kill :44 | |||
Killing Xvnc process ID 27644 | |||
</source> | |||
If you have multiple vncservers running on a node, you may kill them all by running <code>pkill Xvnc -u $USER</code>. | |||
== Multiple connections == <!--T:100--> | |||
<!--T:101--> | |||
All vncserver(s) running under your username (on a login or compute node) can be displayed with <code>vncserver -list</code>. If a vncserver was started with the additional <code>-AlwaysShared</code> option then multiple connections to it can be made by establishing a new tunnel and vncviewer from any remote location. Thus one could leave vncviewer running at the office and then re-connect again from home to access the same desktop and then for example seamlessly continue working with the same applications without closing them. If however a vncserver was not started with <code>vncserver -AlwaysShared</code> then only one vncviewer connection will be possible and additional connection attempts will immediately fail. | |||
== Failures to connect == <!--T:102--> | |||
<!--T:103--> | |||
Repeated failing attempts to establish a new vncserver/vncviewer connection may be due to an old SSH tunnel still running on your desktop tying up ports. To identify and kill any such tunnels, open a terminal window on your desktop and run <code>ps ux | grep ssh</code> followed by <code>kill PID</code>. | |||
== Unlock screensaver == <!--T:104--> | |||
<!--T:105--> | |||
If your VNC screensaver times out and requests a password, enter your cluster account password to unlock it (not your vncserver password). If you are running the MATE desktop and the screensaver will not unlock, try running <code>killall -9 .mate-screensaver</code>. This should no longer be a problem on our clusters as the VNC screensaver has been disabled. | |||
= Software = <!--T:106--> | |||
<!--T:107--> | |||
The VDI nodes support direct vncviewer connections and GPU-accelerated OpenGL graphics for appropriately-configured software applications. The VDI nodes also provide an extra set of software modules in the SnEnv environment, analogous to the StdEnv environments available on all our clusters.<br><br> | |||
On regular login nodes, a standard software environment and some default modules are automatically loaded when you log in. This is not so on a VDI node, thus you will see: | |||
<!--T:176--> | |||
{{Command|prompt=[name@gra-vdi4]$ | |||
|module list | |||
|result= | |||
No modules loaded | |||
}} | |||
<!--T:177--> | |||
Therefore, before running any graphical software on gra-vdi you must first manually load one of the following | |||
== StdEnv == <!--T:130--> | |||
<!--T:131--> | |||
Most users will find it sufficient to load the StdEnv module on gra-vdi. Doing so will provide access to the same software modules that are loaded by default on the clusters: | |||
<!--T:178--> | |||
{{Commands|prompt=[name@gra-vdi4]$ | |||
|module load CcEnv StdEnv/2023 | |||
|module avail | |||
}} | |||
== SnEnv == <!--T:132--> | |||
<!--T:155--> | |||
In some rare cases users will need to load a locally installed module(s) on gra-vdi. To do this the <code>SnEnv</code> must first be loaded: | |||
<!--T:156--> | |||
{{Commands|prompt=[name@gra-vdi4]$ | |||
|module load SnEnv | |||
|module avail | |||
}} | }} | ||
== NIX == <!--T:108--> | |||
{{Commands | <!--T:110--> | ||
|module load | Instead of loading SnEnv or StdEnv users may want to load the <code>nix</code> module which provides open-source software that is optimized to use accelerated OpenGL whenever possible. This module is only available on graham and gra-vdi and can be loaded as follows: | ||
<!--T:151--> | |||
{{Commands|prompt=[name@gra-vdi4]$ | |||
|module load nix | |||
}} | }} | ||
<!--T:112--> | |||
The nix and nix-env commands will now be in your path to manage software packages via NIX within your personal nix environment. | |||
<!--T:114--> | |||
<b>Installing software</b> | |||
<!--T:116--> | |||
To install a nix package into your environment, click the black terminal icon on the top menu bar or select <i>Applications -> System Tools -> Terminal</i>. Once a terminal window appears, run <code>module load nix</code>. You can now search for programs using the <code>nix search <regexp></code> command and install them in your environment using the <code>nix-env --install --attr <attribute></code> command. As an example, to install [https://qgis.org QGIS] do the following: | |||
<!--T:152--> | |||
{{Commands|prompt=[name@gra-vdi4]$ | |||
|nix search qgis | |||
|result= | |||
Attribute name: nixpkgs.qgis | |||
Package name: qgis | |||
Version: 2.18.20 | |||
Description: User friendly Open Source Geographic Information System | |||
}} | |||
{{Commands|prompt=[name@gra-vdi4]$ | |||
|nix-env --install --attr nixpkgs.qgis | |||
}} | |||
<!--T:118--> | |||
Your nix environment persists from one login to the next, so you only need to run an install command once. For example: | |||
<!--T:153--> | |||
{{Commands|prompt=[name@gra-vdi4]$ | |||
|module load nix | |||
|qgis}} | |||
<!--T:120--> | |||
works! In summary whatever software you install today will be available next time you load the nix module. | |||
<!--T:122--> | |||
<b>OpenGL applications</b> | |||
<!--T:124--> | |||
For accelerated OpenGL to work, it is necessary to adjust compiled binaries to pre-load "vglfaker.so" from VirtualGL. This level of customization is automatically done for you on gra-vdi when you install any OpenGL based software package with nix. It is however something that must be done manually after you download and install any software from outside of nix. To do this we suggest using the <code>patchelf</code> utility to adjust the final binary. It can be installed into nix with <code>nix-env --install --attr nixpkgs.patchelf</code> if it's not already on the system. Then once you have built your OpenGL application against the system libraries and for example installed it as ''~/.local/bin/myglapp'' you can add the VirtualGL system library ''/usr/lib64/VirtualGL/libvglfaker.so'' by running: | |||
<!--T:154--> | |||
{{Commands|prompt=[name@gra-vdi4]$ | |||
|module load nix | |||
|patchelf --add-needed /usr/lib64/VirtualGL/libvglfaker.so ~/.local/bin/myglapp | |||
}} | |||
<!--T:128--> | |||
Note that it is also possible to preload ''vglfaker.so'' via the <code>LD_PRELOAD</code> environment variable. This is generally a bad idea as it applies indiscriminately to all binaries, and those that require a different ''vglfaker.so'' than that set in <code>LD_PRELOAD</code> will then fail. It can be used safely in some cases in wrapper scripts. | |||
</translate> | |||
Latest revision as of 19:52, 9 September 2024
It is often necessary to remotely start the graphical user interface for complex software packages such as MATLAB. The most common way to do this is with SSH and X11 forwarding. However the performance of SSH+X11 is often too slow similar to MobaXTerm or Putty. A much better alternative is to use VNC to connect to a remote desktop.
Setup
First you will need to install a VNC client on your machine to connect to the VNC server. We recommend using TigerVNC. A TigerVNC package is available for Windows, MacOS and most Linux distributions. The following shows how to download, install and configure TigerVNC securely for each operating system. The certificate configuration steps are only required for connecting to VDI nodes so the signing authority of the certificate presented by the vncserver is known. If a popup about a certificate issue occurs, either you have not configured it properly or you are not connected to our server and should not enter your password.
Windows
Download and run the latest stable vncviewer64-x.y.z.exe version package installer from the official download page ( for example vncviewer64-1.12.0.exe). Make sure you download the viewer and not the server. To create secure tunnels from your desktop to the vncserver as described in the sections below, you will need to open a terminal window and run the SSH command. This may be done using PowerShell standard on Windows 10 since the 1809 update.
MacOS
Install the latest stable DMG package by going to the official download page and click the green Download Latest Version button for TigerVNC-1.12.90.dmg (as of January 2023). Once the download is complete double click the DMG file to open it. A TigerVNC Viewer icon should appear in a popup window along with a LICENSE.TXT and README.rst file. To complete the installation, drag the tigervnc icon that appears into the Applications folder and/or the lower app dock. To remove the popup you will need to unmount the DMG file. To do this open a New Finder Window, verify View->ShowSidebar is selected, click the small up arrow beside TigerVNC-1.12.90 in the left side menu and lastly close the finder window. If you are running macOS Monterey 12.2 and TigerVNC crashes then you must upgrade to this latest version.
Linux
First install TigerVNC viewer with the package manager for your Linux version:
| Linux Version | Install Command |
|---|---|
| Debian, Ubuntu | sudo apt-get install tigervnc-viewer
|
| Fedora, CentOS, or RHEL | sudo yum install tigervnc
|
| Gentoo | emerge -av net-misc/tigervnc
|
Next, start TigerVNC by either finding it in the applications menu or running vncviewer on the command line. In the "VNC Viewer: Connection Details" window that appears click "Options -> Security" then tick all boxes except "Encryption None" and enter one of the following paths in the "Path to X509 CA Certificate" field.
| Linux Version | Path to X509 CA Certificate |
|---|---|
| Debian, Ubuntu | /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt |
| Fedora, CentOS, or RHEL | /etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt |
| Gentoo | /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt |
To save the settings click OK and then click Connect. If Connect is not clicked, the settings will not be saved.
Connect
Now you need a VNC server to connect to. This can be either a persistent vncserver running on dedicated VDI nodes which are part of Graham, or a temporary vncserver you start on a cluster compute node. VNC is not a heavyweight server, so you can certainly run lightweight sessions on cluster login nodes.
VDI nodes
Graham has two dedicated VDI (aka Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) nodes collectively known as gra-vdi. These nodes provide a remote desktop environment equipped with accelerated OpenGL. They are intended for the most demanding and complex interactive graphical tasks. The VDI nodes share Graham's /home, /project, and /scratch filesystems. As a result, any data files or directories created on graham by running jobs in the queue will immediately be accessible on gra-vdi for visualization and post-processing purposes without the need to transfer them over.
To connect to gra-vdi, start VNC viewer (tigervnc) on your laptop and enter VNC server: gra-vdi.alliancecan.ca. This will bring up a login screen where you can enter your Alliance credentials. A desktop session will then be started on either gra-vdi3 or gra-vdi4 using a round robin algorithm.
Users can also connect directly to either machine by specifying VNC server: gra-vdi3.sharcnet.ca or enter VNC server: gra-vdi4.sharcnet.ca. This may be useful if you find one machine is overloaded (oversubscribed) and thus not very responsive. Or if you consistently want to use the local $SCRATCH directory (defined as /local/tmp/$USER) on one server but not the other. Notice that $SCRATCH is defined differently on the clusters (as /scratch/$USER) where it is shared by all nodes. Similar to the clusters however, any data left on $SCRATCH on gra-vdi will eventually be deleted since the disc space is limited. Please do not plan to store any files on $SCRATCH for more than 60 days!
Lastly, please keep in mind the VDI nodes are a shared resource and intended for visualization tasks. If you need to perform long-running computations within an application which uses a GUI (graphical user interface), then please log out of gra-vdi and instead connect to a compute node on any cluster as described in the Compute Nodes section below. This will ensure the memory and CPU resources on gra-vdi remain fully available for other users to conduct their own simultaneous graphical work without any noticeable performance impacts.
Login nodes
If you want to run a lightweight application in a remote VNC desktop (one that does not require much memory, cputime or a gpu since login node limits will apply here) you may start a VNC server on a cluster login node (such as graham) and then connect to it with the following procedure:
[laptop:~] ssh graham.alliancecan.ca
1) Since moving to turbovnc on the clusters, the -maxconnectiontime vncserver option is no longer supported. Instead use vncserver -idletimeout seconds to ensure your session is eventually killed. This will ensure any unnecessarily consumed system resources associated with your desktop (such as memory) will be released. The first time you start vncserver you will be required to set a password which can be changed later. The password will be required to remotely connect to your desktop with a vncclient (such as vncviewer). Likewise the password will be required when making multiple connections assuming you started vncserver with the additional -alwaysshared option shown here (the square brackets mean optional and should not be included):
[gra-login2:~] vncserver -idletimeout 604800 [-alwaysshared] Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? n Desktop 'TurboVNC: gra-login2:2 (username)' started on display gra-login2:2 Starting applications specified in /cvmfs/soft.computecanada.ca/gentoo/2023/x86-64-v3/usr/bin/xstartup.turbovnc Log file is /home/username/.vnc/gra-login2:2.log
2) Determine the listening port (5903 in this example):
[gra-login2:~] grep -iE "\sport|kill" /home/username/.vnc/gra-login2:2.log 03/09/2024 17:48:40 Listening for VNC connections on TCP port 5903
[gra-login2:~] exit
3) Open a terminal window on your desktop and start a SSH tunnel to the VNC server:
[laptop:~] ssh graham.computecanada.ca -L 5901:gra-login2:5903
4) Open another terminal window on your desktop and connect with vncviewer:
[laptop:~] vncviewer localhost:5901
Mac or Windows users should click the TigerVNC Viewer application icon on their desktop and enter the localhost:port information in the "Connection Details" dialogue box that appears. Keep in mind that strict memory and cputime limits apply on cluster login nodes. On Graham, these are 8GB and 1 cpu-hour per process according to ulimit -t -v. If you require more resources, then run your VNC server on the VDI nodes or compute nodes instead as described above and below respectively.
Compute nodes
Where VDI login nodes are unavailable you can start a VNC server on a compute node, and with suitable port forwarding, connect to it from your desktop. This gives you dedicated access to the server, but does not provide a full graphical desktop or hardware-accelerated OpenGL.
1) Start a VNC server
Before starting your VNC server, log in to a cluster (such as Cedar) and create an allocation on a compute node using the salloc command (a 24hr maximum time limit applies). For example, to request an interactive job using 4 CPUs and 16GB of memory you could use the command:
[username@cedar5:~/project] salloc --time=1:00:00 --cpus-per-task=4 --mem=16000 --account=def-username
salloc: Pending job allocation 20067316
salloc: job 20067316 queued and waiting for resources
salloc: job 20067316 has been allocated resources
salloc: Granted job allocation 20067316
salloc: Waiting for resource configuration
salloc: Nodes cdr768 are ready for job
[username@cdr768:~/project]
Once your interactive job has started, one environment variable must be set in order to avoid some repetitive desktop errors:
[username@cdr768:~/project] export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=${SLURM_TMPDIR}
Then, start a VNC server with vncserver. Take note of which node your job is running on. If unsure, you can use the hostname command to check. The first time you do this you will be prompted to set a password for your VNC server. DO NOT LEAVE THIS BLANK. You may change it later using the vncpasswd command. Continuing with the example:
[username@cdr768:~/project] vncserver
You will require a password to access your desktops.
Password:
Verify:
Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? n
xauth: file /home/username/.Xauthority does not exist
New 'cdr768.int.cedar.computecanada.ca:1 (username)' desktop is cdr768.int.cedar.computecanada.ca:1
Creating default startup script /home/username/.vnc/xstartup
Creating default config /home/username/.vnc/config
Starting applications specified in /home/username/.vnc/xstartup
Log file is /home/username/.vnc/cdr768.int.cedar.computecanada.ca:1.log
Determine which port the VNC server is using by examining the log file:
[username@cdr768:~/project] grep -iE "\sport|kill" /home/username/.vnc/cdr768.int.cedar.computecanada.ca:1.log
vncext: Listening for VNC connections on all interface(s), port 5901
2) Set up a SSH tunnel to the VNC server
Once your VNC server has been started, create a "bridge" to allow your local desktop computer to connect to the compute node directly. This bridge connection is created using an SSH tunnel. SSH tunnels are created on your computer in a new local terminal window using the same SSH connection command as usual, with an extra option added which follows the format ssh user@host -L port:compute_node:port.
An example of an SSH tunnel command run on your computer to connect to a VNC server running on Cedar's cdr768 node and port 5901 would be the following:
[name@local_computer]$ ssh username@cedar.computecanada.ca -L 5902:cdr768:5901
The SSH tunnel operates like a normal SSH session: You may run commands over it, etc. However, keep in mind that this SSH session is also your connection to the VNC server. If you terminate the SSH session, your connection to the VNC server will be lost! For more information, please see SSH tunnelling.
3) Connect to the VNC server
If you have a Linux desktop, open a new local terminal window and tell your VNC client to connect to localhost:port. The following example uses the TigerVNC vncviewer command to connect to the running VNC server on cdr768. You will be prompted for the VNC password that you set up earlier in order to connect.
[name@local_computer]$ vncviewer localhost:5902
TigerVNC Viewer 64-bit v1.8.0
Built on: 2018-06-13 10:56
Copyright (C) 1999-2017 TigerVNC Team and many others (see README.txt)
See http://www.tigervnc.org for information on TigerVNC.
Tue Jul 10 17:40:24 2018
DecodeManager: Detected 8 CPU core(s)
DecodeManager: Creating 4 decoder thread(s)
CConn: connected to host localhost port 5902
CConnection: Server supports RFB protocol version 3.8
CConnection: Using RFB protocol version 3.8
CConnection: Choosing security type VeNCrypt(19)
CVeNCrypt: Choosing security type TLSVnc (258)
Tue Jul 10 17:40:27 2018
CConn: Using pixel format depth 24 (32bpp) little-endian rgb888
CConn: Using Tight encoding
CConn: Enabling continuous updates
If you are on a Mac or Windows desktop, click the TigerVNC Viewer application icon and enter the localhost:port information. For our example it becomes: 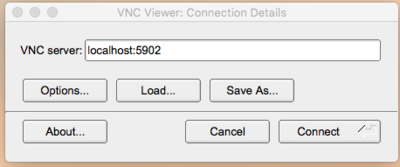
Please note the port number in localhost:port specified above (5902) must match the local port (the first number) you specified when you set up the SSH tunnel. The default VNC port is 5900. If you specified 5900 for the local port of the SSH tunnel, you could omit it when you invoke vncviewer. However, Windows users may find that they cannot set up an SSH tunnel on local port 5900. Once connected, you will be presented with a Linux MATE desktop. To launch a terminal, click on the top menu on "Applications -> System Tools -> MATE Terminal". You may also add a shortcut to the top menu by right-clicking on "MATE Terminal" and by clicking on "Add this launcher to panel". Finally, to launch a program, invoke the command as you would normally within a bash session, for example xclock. To start a more complicated program like MATLAB, load the module and then run the matlab command.
More information
Vncserver password
To reset your VNC server password, use the vncpasswd command:
[gra-login1:~] vncpasswd
Password:
Verify:
Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? n
Optionally you can completely remove your VNC configuration (including your password) by deleting your ~/.vnc directory. The next time you run vncserver you will be prompted to set a new password.
Killing vncserver
If a vncserver is no longer needed, terminate it with vncserver -kill :DISPLAY# as shown here:
[gra-login1:~] vncserver -list
TigerVNC server sessions:
X DISPLAY# PROCESS ID
:44 27644
[gra-login1:~] vncserver -kill :44
Killing Xvnc process ID 27644
If you have multiple vncservers running on a node, you may kill them all by running pkill Xvnc -u $USER.
Multiple connections
All vncserver(s) running under your username (on a login or compute node) can be displayed with vncserver -list. If a vncserver was started with the additional -AlwaysShared option then multiple connections to it can be made by establishing a new tunnel and vncviewer from any remote location. Thus one could leave vncviewer running at the office and then re-connect again from home to access the same desktop and then for example seamlessly continue working with the same applications without closing them. If however a vncserver was not started with vncserver -AlwaysShared then only one vncviewer connection will be possible and additional connection attempts will immediately fail.
Failures to connect
Repeated failing attempts to establish a new vncserver/vncviewer connection may be due to an old SSH tunnel still running on your desktop tying up ports. To identify and kill any such tunnels, open a terminal window on your desktop and run ps ux | grep ssh followed by kill PID.
Unlock screensaver
If your VNC screensaver times out and requests a password, enter your cluster account password to unlock it (not your vncserver password). If you are running the MATE desktop and the screensaver will not unlock, try running killall -9 .mate-screensaver. This should no longer be a problem on our clusters as the VNC screensaver has been disabled.
Software
The VDI nodes support direct vncviewer connections and GPU-accelerated OpenGL graphics for appropriately-configured software applications. The VDI nodes also provide an extra set of software modules in the SnEnv environment, analogous to the StdEnv environments available on all our clusters.
On regular login nodes, a standard software environment and some default modules are automatically loaded when you log in. This is not so on a VDI node, thus you will see:
[name@gra-vdi4]$ module list
No modules loaded
Therefore, before running any graphical software on gra-vdi you must first manually load one of the following
StdEnv
Most users will find it sufficient to load the StdEnv module on gra-vdi. Doing so will provide access to the same software modules that are loaded by default on the clusters:
[name@gra-vdi4]$ module load CcEnv StdEnv/2023
[name@gra-vdi4]$ module avail
SnEnv
In some rare cases users will need to load a locally installed module(s) on gra-vdi. To do this the SnEnv must first be loaded:
[name@gra-vdi4]$ module load SnEnv
[name@gra-vdi4]$ module avail
NIX
Instead of loading SnEnv or StdEnv users may want to load the nix module which provides open-source software that is optimized to use accelerated OpenGL whenever possible. This module is only available on graham and gra-vdi and can be loaded as follows:
[name@gra-vdi4]$ module load nix
The nix and nix-env commands will now be in your path to manage software packages via NIX within your personal nix environment.
Installing software
To install a nix package into your environment, click the black terminal icon on the top menu bar or select Applications -> System Tools -> Terminal. Once a terminal window appears, run module load nix. You can now search for programs using the nix search <regexp> command and install them in your environment using the nix-env --install --attr <attribute> command. As an example, to install QGIS do the following:
[name@gra-vdi4]$ nix search qgis
[name@gra-vdi4]$ nix-env --install --attr nixpkgs.qgis
Your nix environment persists from one login to the next, so you only need to run an install command once. For example:
[name@gra-vdi4]$ module load nix
[name@gra-vdi4]$ qgis
works! In summary whatever software you install today will be available next time you load the nix module.
OpenGL applications
For accelerated OpenGL to work, it is necessary to adjust compiled binaries to pre-load "vglfaker.so" from VirtualGL. This level of customization is automatically done for you on gra-vdi when you install any OpenGL based software package with nix. It is however something that must be done manually after you download and install any software from outside of nix. To do this we suggest using the patchelf utility to adjust the final binary. It can be installed into nix with nix-env --install --attr nixpkgs.patchelf if it's not already on the system. Then once you have built your OpenGL application against the system libraries and for example installed it as ~/.local/bin/myglapp you can add the VirtualGL system library /usr/lib64/VirtualGL/libvglfaker.so by running:
[name@gra-vdi4]$ module load nix
[name@gra-vdi4]$ patchelf --add-needed /usr/lib64/VirtualGL/libvglfaker.so ~/.local/bin/myglapp
Note that it is also possible to preload vglfaker.so via the LD_PRELOAD environment variable. This is generally a bad idea as it applies indiscriminately to all binaries, and those that require a different vglfaker.so than that set in LD_PRELOAD will then fail. It can be used safely in some cases in wrapper scripts.