Arbutus object storage clients: Difference between revisions
(removed "provided by the Arbutus team" because keys are now self-service, no longer provided by the team) |
m (Mboisson a déplacé la page Arbutus Object Storage Clients vers Arbutus object storage clients sans laisser de redirection: Part of translatable page "Arbutus Object Storage Clients") |
(No difference)
| |
Revision as of 20:38, 17 February 2023
For information on obtaining Arbutus Object Storage, please see this page. Below, we describe how to configure and use three common object storage clients:
- s3cmd
- WinSCP
- awscli
It is important to note that Arbutus' Object Storage solution does not use Amazon's S3 Virtual Hosting (i.e. DNS-based bucket) approach which these clients assume by default. They need to be configured not to use that approach as described below.
s3cmd[edit]
Installing s3cmd[edit]
Depending on your Linux distribution, the s3cmd command can be installed using the appropriate yum (RHEL, CentOS) or apt (Debian, Ubuntu) command:
$ sudo yum install s3cmd
$ sudo apt install s3cmd
Configuring s3cmd[edit]
To configure the s3cmd tool use the command:
$ s3cmd --configure
And make the following configurations with the keys provided or created with the openstack ec2 credentials create command:
Enter new values or accept defaults in brackets with Enter. Refer to user manual for detailed description of all options. Access key and Secret key are your identifiers for Amazon S3. Leave them empty for using the env variables. Access Key []: 20_DIGIT_ACCESS_KEY Secret Key []: 40_DIGIT_SECRET_KEY Default Region [US]: Use "s3.amazonaws.com" for S3 Endpoint and not modify it to the target Amazon S3. S3 Endpoint []: object-arbutus.cloud.computecanada.ca Use "%(bucket)s.s3.amazonaws.com" to the target Amazon S3. "%(bucket)s" and "%(location)s" vars can be used if the target S3 system supports dns based buckets. DNS-style bucket+hostname:port template for accessing a bucket []: object-arbutus.cloud.computecanada.ca Encryption password is used to protect your files from reading by unauthorized persons while in transfer to S3 Encryption password []: PASSWORD Path to GPG program []: /usr/bin/gpg When using secure HTTPS protocol all communication with Amazon S3 servers is protected from 3rd party eavesdropping. This method is slower than plain HTTP, and can only be proxied with Python 2.7 or newer Use HTTPS protocol []: Yes On some networks all internet access must go through a HTTP proxy. Try setting it here if you can't connect to S3 directly HTTP Proxy server name:
Create buckets[edit]
The next task is to make a bucket. Buckets contain files. Bucket names must be unique across the Arbutus object storage solution. Therefore, you will need to create a uniquely named bucket which will not conflict with other users. For example, buckets s3://test/ and s3://data/ are likely already taken. Consider creating buckets reflective of your project, for example s3://def-test-bucket1 or s3://atlas_project_bucket. Valid bucket names may only use the upper case characters, lower case characters, digits, periods, hyphens, and underscores (i.e. A-Z, a-z, 0-9, ., -, and _ ).
To create a bucket, use the tool's mb (make bucket) command:
$ s3cmd mb s3://BUCKET_NAME/
To see the status of a bucket, use the info command:
$ s3cmd info s3://BUCKET_NAME/
The output will look something like this:
s3://BUCKET_NAME/ (bucket): Location: default Payer: BucketOwner Expiration Rule: none Policy: none CORS: none ACL: *anon*: READ ACL: USER: FULL_CONTROL URL: http://object-arbutus.cloud.computecanada.ca/BUCKET_NAME/
Upload files[edit]
To upload a file to the bucket, use the put command similar to this:
$ s3cmd put --guess-mime-type FILE_NAME.dat s3://BUCKET_NAME/FILE_NAME.dat
Where the bucket name and the file name are specified. Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) is a mechanism for handling files based on their type. The --guess-mime-type command parameter will guess the MIME type based on the file extension. The default MIME type is binary/octet-stream.
Delete File[edit]
To delete a file from the bucket, use the rm command similar to this:
$ s3cmd rm s3://BUCKET_NAME/FILE_NAME.dat
Access Control Lists (ACLs) and Policies[edit]
Buckets can have ACLs and policies which govern who can access what resources in the object store. These features are quite sophisticated. Here are two simple examples of using ACLs using the tool's setacl command.
$ s3cmd setacl --acl-public -r s3://BUCKET_NAME/
The result of this command is that the public can access the bucket and recursively (-r) every file in the bucket. Files can be accessed via URLs such as
https://object-arbutus.cloud.computecanada.ca/BUCKET_NAME/FILE_NAME.dat
The second ACL example limits access to the bucket to only the owner:
$ s3cmd setacl --acl-private s3://BUCKET_NAME/
Other more sophisticated examples can be found in the s3cmd help site or s3cmd(1) man page.
WinSCP[edit]
Installing WinSCP[edit]
WinSCP can be installed from https://winscp.net/.
Configuring WinSCP[edit]
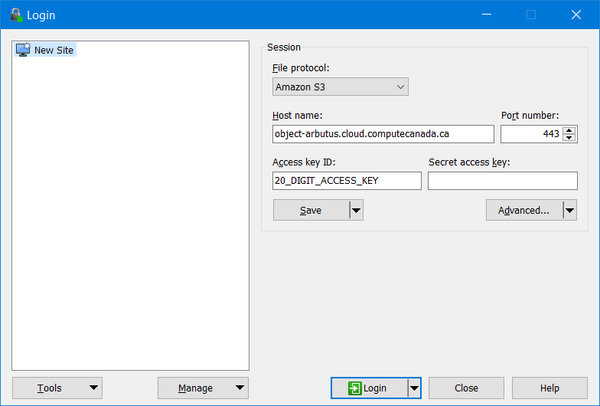
Under "New Session", make the following configurations:
- File protocol: Amazon S3
- Host name: object-arbutus.cloud.computecanada.ca
- Port number: 443
- Access key ID: 20_DIGIT_ACCESS_KEY
and "Save" these settings as shown below
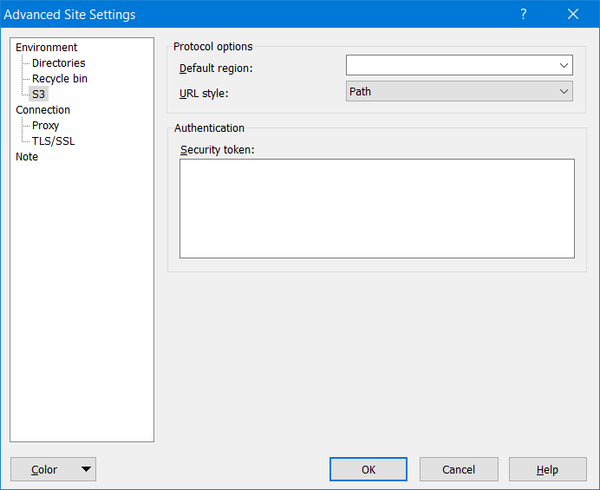
Next, click on the "Edit" button and then click on "Advanced..." and navigate to "Environment" to "S3" to "Protocol options" to "URL style:" which must changed from "Virtual Host" to "Path" as shown below:
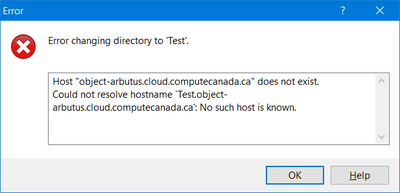
This "Path" setting is important, otherwise WinSCP will not work and you will see hostname resolution errors, like this:
Using WinSCP[edit]
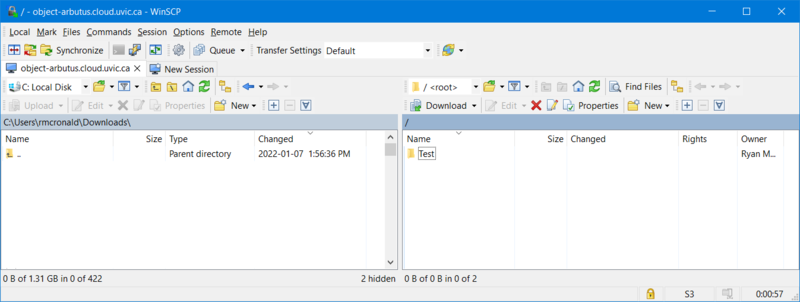
Click on the "Login" button and use the WinSCP GUI to create buckets and to transfer files:
Access Control Lists (ACLs) and Policies[edit]
Right-clicking on a file will allow you to set a file's ACL, like this:
AWS CLI[edit]
The awscli client also works with the Object Store service with better support for large (>5GB) files and the helpful sync command. However, not all features have not been tested.
Installing awscli[edit]
pip install awscli awscli-plugin-endpoint
Configuring awscli[edit]
Generate an access key ID & secret key
openstack ec2 credentials create
Edit or create ~/.aws/credentials and add the credentials generated above
[default] aws_access_key_id = <access_key> aws_secret_access_key = <secret_key>
Edit ~/.aws/config and add the following configuration
[plugins] endpoint = awscli_plugin_endpoint [profile default] s3 = endpoint_url = https://object-arbutus.cloud.computecanada.ca signature_version = s3v4 s3api = endpoint_url = https://object-arbutus.cloud.computecanada.ca
Using awscli[edit]
export AWS_PROFILE=default aws s3 ls <container-name> aws s3 sync local_directory s3://container-name/prefix
More examples can be found here: https://docs.ovh.com/us/en/storage/getting_started_with_the_swift_S3_API/