Transferring data: Difference between revisions
(Marked this version for translation) |
(mention curl) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
==From the World Wide Web== <!--T:5--> | ==From the World Wide Web== <!--T:5--> | ||
The standard tool for downloading data from websites is [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wget wget]. | The standard tool for downloading data from websites is [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wget wget]. Also available is [https://curl.haxx.se/ curl]. The two are compared in this [https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/47434/what-is-the-difference-between-curl-and-wget StackExchange article]. | ||
==Synchronizing files== <!--T:6--> | ==Synchronizing files== <!--T:6--> | ||
Revision as of 14:21, 28 September 2017
To and from your personal computer[edit]
You will need software that supports secure transfer of files between your computer and the Compute Canada machines. The commands scp and sftp can be used in a command-line environment on Linux or Mac OS X computers. On Microsoft Windows platforms, MobaXterm offers both a graphical file transfer function and a command-line interface via SSH, while WinSCP is another free program that supports file transfer. PuTTY comes with pscp and psftp which are essentially the same as the Linux and Mac command line programs.
If it takes more than one minute to move your files to or from Compute Canada servers, we recommend you install and try Globus Personal Connect. Globus transfers can be set up and will go on in the background without you. Most Compute Canada legacy systems can be reached with Globus.
Between Compute Canada resources[edit]
Globus is the preferred tool for transferring data between Compute Canada systems, and if it can be used, it should.
However, other common tools can also be found for transferring data both inside and outside of Compute Canada, including
From the World Wide Web[edit]
The standard tool for downloading data from websites is wget. Also available is curl. The two are compared in this StackExchange article.
Synchronizing files[edit]
To synchronize or "sync" files (or directories) stored in two different locations means to ensure that the two copies are the same. Here are several different ways to do this.
Globus Transfer[edit]
We find Globus usually gives the best performance and reliability.
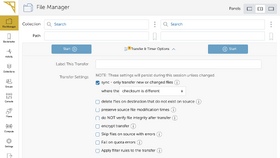
Normally when a Globus transfer is initiated it will overwrite the files on the destination with the files from the source, which means all of the files on the source will be transferred. If some of the files may already exist on the destination and need not be transferred if they match, you should go to the bottom of the transfer window as shown in the screenshot and choose to "sync" instead.
You may choose how Globus decides which files to transfer:
| Their checksums are different | This is the slowest option but most accurate. This will catch changes or errors that result in the same size of file, but with different contents. |
| File doesn't exist on destination | This will only transfer files that have been created since the last sync. Useful if you are incrementally creating files. |
| File size is different | A quick test. If the file size has changed then its contents must have changed, and it will be re-transferred. |
| Modification time is newer | This will check the file's recorded modification time and only transfer the file if it is newer on the source than the destination. If you want to depend on this it is important to check the "preserve source file modification times" option when initiating a Globus Transfer. |
For more information about Globus please see Globus.
Rsync[edit]
Rsync is a popular tool for ensuring that two separate datasets are the same but can be quite slow if there are a lot of files or there is a lot of latency between the two sites, i.e. they are geographically apart or on different networks. Running rsync will check the modification time and size of each file, and will only transfer the file if one or the other does not match. If you expect modification times not to match on the two systems you can use the "-c" option, which will compute checksums at the source and destination, and transfer only if the checksums do not match.
When using rsync to transfer to /project if you encounter the message Disk quota exceeded ensure you have not included the p option, either directly or indirectly with the a option as this can cause the group ID of the file to be incorrectly set. The group ID is used to apply a file's size towards a project quota.
Using checksums to check if files match[edit]
If Globus is unavailable between the two systems being synchronized and Rsync is taking too long, then you can use a checksum utility on both systems to determine if the files match. In this example we use sha1sum.
[name@server ~]$ find /home/username/ -type f -print0 | xargs -0 sha1sum | tee checksum-result.log
This command will create a new file called checksum-result.log in the current directory; the file will contain all of the checksums for the files in /home/username/. It will also print out all of the checksums to the screen as it goes. If you have a lot of files or very large files you may want to run this command in the background, in a screen or tmux session; anything that allows it to continue if your SSH connection times out.
After you run it on both systems you can use the diff utility to find files that don't match.
[name@server ~]$ diff checksum-result-silo.log checksum-dtn.log
69c69
< 017f14f6a1a194a5f791836d93d14beead0a5115 /home/username/file-0025048576-0000008
---
> 8836913c2cc2272c017d0455f70cf0d698daadb3 /home/username/file-0025048576-0000008
It is possible that the find command will crawl through the directories in a different order resulting in a lot of false differences so you may need to run sort on both files before running diff such as:
[name@server ~]$ sort -k2 checksum-result-silo.log -o checksum-result-silo.log
[name@server ~]$ sort -k2 checksum-dtn.log -o checksum-dtn.log
SFTP[edit]
SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) uses the SSH protocol to transfer files between machines which encrypts data being transferred.
For example you can connect to a remote machine at ADDRESS as user USERNAME with SFTP to transfer files like so:
[name@server]$ sftp USERNAME@ADDRESS
The authenticity of host 'ADDRESS (###.###.###.##)' can't be established.
RSA key fingerprint is ##:##:##:##:##:##:##:##:##:##:##:##:##:##:##:##.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added 'ADDRESS,###.###.###.##' (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
USERNAME@ADDRESS's password:
Connected to ADDRESS.
sftp>
or using an SSH Key for authentication using the -i option
[name@server]$ sftp -i /home/name/.ssh/id_rsa USERNAME@ADDRESS
Connected to ADDRESS.
sftp>
which returns the sftp> prompt where commands to transfer files can be issued. To get a list of commands available to use at the sftp prompt enter the help command.
There are also a number of graphical programs available for Windows, Linux and Mac OS, such as WinSCP and MobaXterm (Windows), filezilla (Windows,Mac, and Linux), and cyberduck (Mac and Windows).