QGIS: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(added QT_QPA_PLATFORM=offscreen env to batch job; seems required to avoid graphical output depenencies) |
||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
module load qgis | module load qgis | ||
export QT_QPA_PLATFORM=offscreen | |||
python qgis_code.py | python qgis_code.py | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:47, 13 May 2024
This is not a complete article: This is a draft, a work in progress that is intended to be published into an article, which may or may not be ready for inclusion in the main wiki. It should not necessarily be considered factual or authoritative.
QGIS is a free and open-source cross-platform desktop geographic information system (GIS) application that supports viewing, editing, and analysis of geospatial data.
IMPORTANT
Never make intense use of QGIS on the login nodes! Submit jobs using the command line whenever possible and if you must visualize your data using the GUI, please do so on an interactive node. Using parallel rendering on the shared login nodes will result in the termination of your session.
Loading QGIS[edit]
You will first need to load gcc
[name@server ~]$ module load gcc/5.4.0
Then, you will need to load the QGIS module; there could potentially be several versions available and you can see a list of all of them using the command
[name@server ~]$ module spider qgis
You can load a particular QGIS module using a command like
[name@server ~]$ module load qgis/2.18.24
You might also have to load various other modules depending on the packages you need to install. For example, "rgdal" will require that you load a module called "gdal", which itself requires that you load nixpkgs and gcc. Nixpkgs should already be loaded by default. You can ensure that it is by running
[name@server ~]$ module list
If nixpkgs is not listed, you can load it by running
[name@server ~]$ module load nixpkgs/16.09
If any package fails to install, be sure to read the error message carefully, as it might give you some details concerning some additional modules you need to load. You can also find out if a module is dependent on any other module by running
[name@server ~]$ module spider gdal/2.2.1
Command-line QGIS[edit]
You can execute QGIS by running a Python script:
[name@server ~]$ python qgis_code.py
1. Place your python code in a script file, in this case the file is called qgis_code.py.
from qgis.core import *
# supply path to qgis install location
QgsApplication.setPrefixPath("/path/to/qgis/installation", True)
# create a reference to the QgsApplication, setting the
# second argument to False disables the GUI
qgs = QgsApplication([], False)
# load providers
qgs.initQgis()
# Write your code here to load some layers, use processing
# algorithms, etc.
# When your script is complete, call exitQgis() to remove the
# provider and layer registries from memory
qgs.exitQgis()
2. Copy the following content in a job submission script called job.sh:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --account=def-someacct # replace this with your own account
#SBATCH --ntasks=1 # number of MPI processes
#SBATCH --mem-per-cpu=2048M # memory; default unit is megabytes
#SBATCH --time=0-00:15 # time (DD-HH:MM)
module load gcc
module load qgis
export QT_QPA_PLATFORM=offscreen
python qgis_code.py
3. Submit the job with:
sbatch job.sh
For more on submitting jobs, see the Running jobs page.
Using the GUI[edit]
You may want to visualize large datasets without having to download them to your desktop. QGIS offers the possibility to use multiple cores to render the maps but you should not use this option on the login nodes which are shared with multiple users. Instead, you should use interactive nodes to do the visualization.
Using the QGIS GUI requires X11 forwarding, which you should make sure is enabled.
MobaXTerm (Windows)[edit]
You can find information on how to connect with MobaXTerm and use X11 fowarding on the Connecting_with_MobaXTerm page.
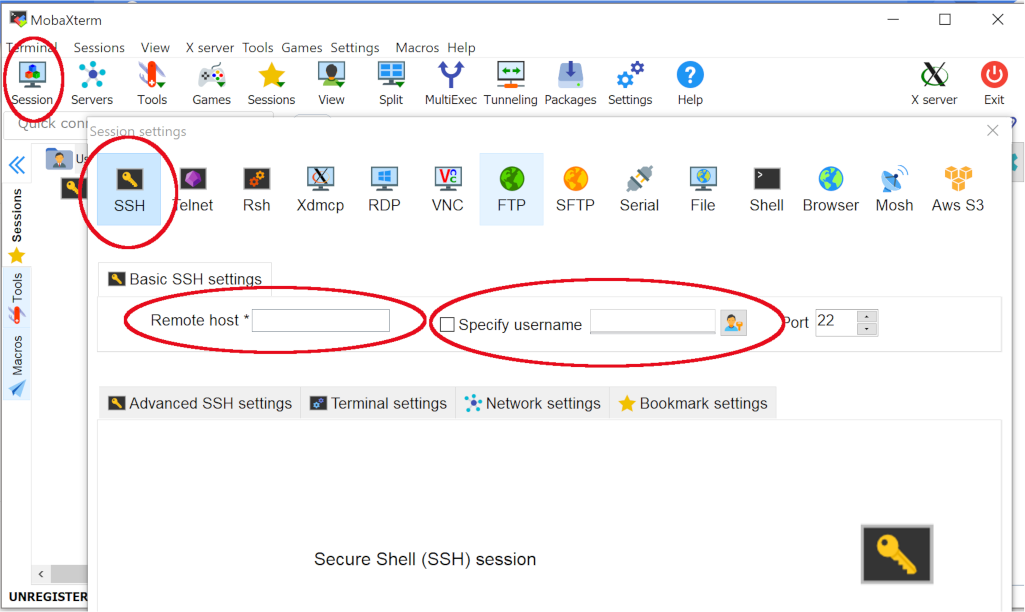
1. In the main window, click "Sessions" and a new window will pop up. Select "SSH".
2. In "Remote host", write the name of the server you plan to use, for example "cedar.computecanada.ca".
3. You can choose to specify a username and write your Compute Canada username. Leave port 22 as it is.
4. A terminal will open and you will be prompted to enter your password. You won't see anything appear as you input your password but it's nothing to worry about.
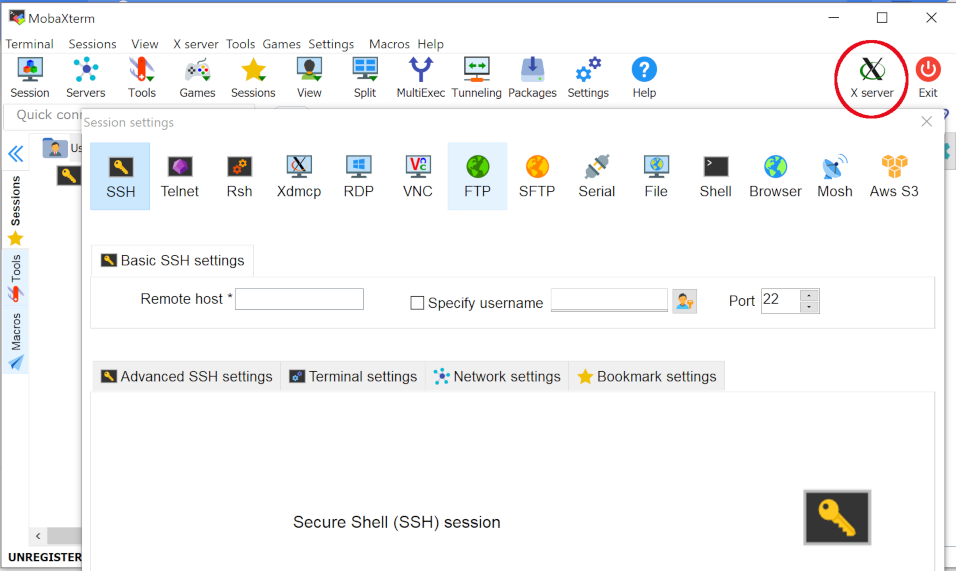
5. Make sure that the X server logo is green and that X11 forwarding is therefore enabled.
6. In the terminal, load gcc and the QGIS module as shown in the section "Loading QGIS".
7. Start QGIS by typing
[name@server ~]$ qgis
8. QGIS should appear in a new window and you are ready to use it.
9. To close QGIS, simply close the window like you usually would.
Terminal (Unix)[edit]
More information to come.
Use an interactive node[edit]
Runtime is limited on the login nodes, so you will need to request a testing job to have more time for exploring and visualizing your data. Additionally, by doing so, you will have access to the 40 cores of each of the nodes requested.
request an interactive job, ie.
[name@login ~]$ salloc --time=1:0:0 --ntasks=2 --x11 --account=def-someuser
this will connect you to a node. Note the --x11 argument, which will enable X11 forwarding on the interactive node.
You can then load QGIS and run it on the interactive node.
[name@server ~]$ module load gcc
[name@server ~]$ module load qgis
[name@server ~]$ qgis
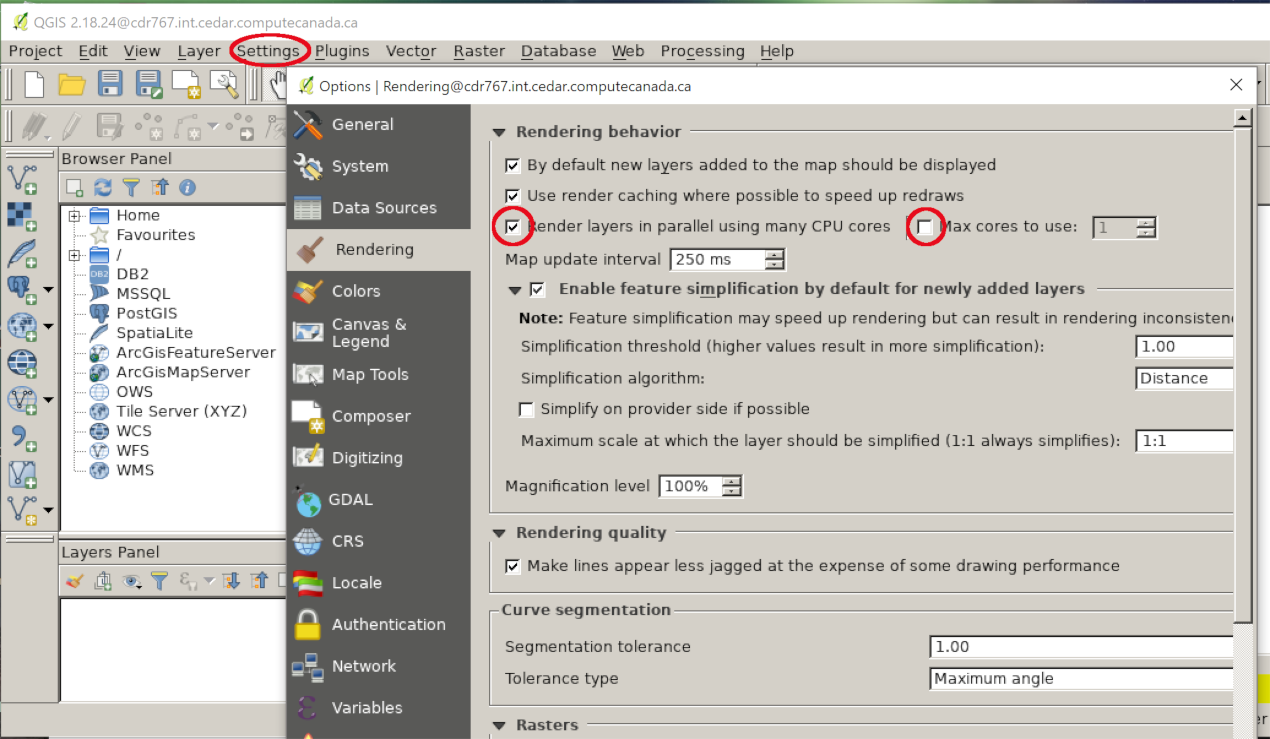
You can enable parallel rendering of the layers by clicking "Settings" and "Options" in the main window, then "Rendering" in the Options window. Check "Render layers in parallel using many CPU cores" and you can select a number of cores to use (optional).
Once you are done and have closed QGIS, you can terminate the allocation
[name@server ~]$ exit