Connecting with PuTTY
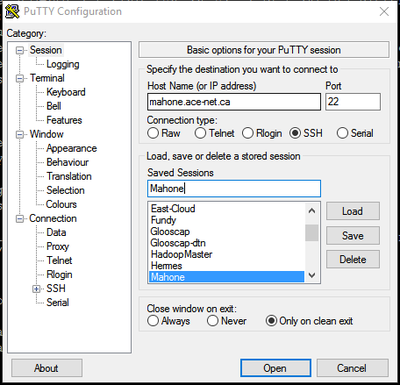
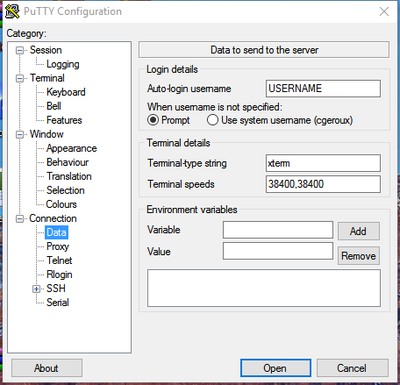
Start up PuTTY and enter the host name or IP address of the machine you wish to connect to. You may also save a settings by entering a session name in the "Save Sessions" text box and clicking the "Save" button. You can set the username to use when logging into a particular host under the Connection->Data section in the Auto-login username text box to saving typing the username when connecting.
X11 Forwarding
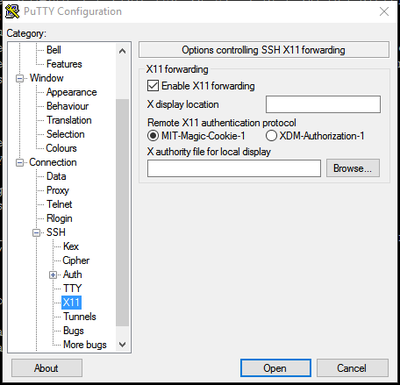
If working with graphical-based programs, X11 forwarding should be enabled. To do this, go to Connection->SSH->X11 and check the "Enable X11 forwarding" checkbox. To use X11 forwarding one must install an "X window server" such as Xming or, for the recent versions of Windows, VcXsrv. The X window server should be actually started prior to connecting with SSH. Test that X11 forwarding is working by opening a PuTTY session and running a simple GUI based program, such as typing the command xclock. If you see a popup window with a clock, X11 forwarding should be working.
Using a Key Pair
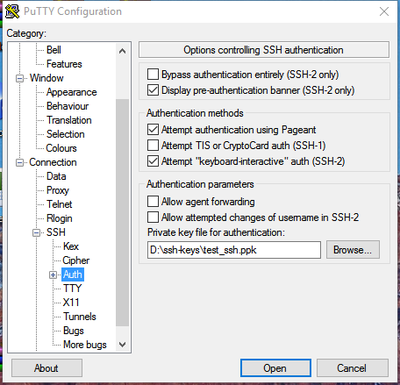
To set the private key putty uses when connecting to a machine go to Connection->SSH->Auth and clicking the "Browse" button to find the private key file to use. Putty uses files with a ".ppk" suffix, which are generated using PuTTYGen (see Generating SSH keys in Windows for instructions on how to create such a key). In newer versions of Putty, you need to click the "+" sign next to "Auth" and then select "Credentials" to be able to browse for the "Private key file for authentication". Note that the additional fields in that newer interface, i.e. "Certificate to use" and "Plugin to provide authentication response", should be left blank.