OpenACC Tutorial - Profiling
- Understand what a profiler is
- Understand how to use the NVPROF profiler
- Understand how the code is performing
- Understand where to focus your time and rewrite most time consuming routines
Code profiling
Why would one need to profile code? Because it's the only way to understand:
- Where time is being spent (hotspots)
- How the code is performing
- Where to focus your development time
What is so important about hotspots in the code? Amdahl's law says that "Parallelizing the most time-consuming routines (i.e. the hotspots) will have the most impact".
Build the Sample Code
For this example we will use code from this Git repository. Download the package and go to the cpp or f90 directory. The object of this exercise is to compile and link the code, obtain an executable, and then profile it.
Being pushed by NVIDIA through its Portland Group division until 2020 and now through its HPC SDK, as well as by Cray, these two lines of compilers offer the most advanced OpenACC support.
As for the GNU Compiler, since GCC version 6, the support for OpenACC 2.x kept improving. As of July 2022, GCC versions 10, 11 and 12 support OpenACC version 2.6.
For the purpose of this tutorial, we use version 22.7 of the NVIDIA HPC SDK. We note that NVIDIA compilers are free for academic usage.
[name@server ~]$ module load nvhpc/22.7
Lmod is automatically replacing "intel/2020.1.217" with "nvhpc/22.7".
The following have been reloaded with a version change:
1) gcccore/.9.3.0 => gcccore/.11.3.0 3) openmpi/4.0.3 => openmpi/4.1.4
2) libfabric/1.10.1 => libfabric/1.15.1 4) ucx/1.8.0 => ucx/1.12.1
[name@server ~]$ make
nvc++ -c -o main.o main.cpp
nvc++ main.o -o cg.x
After the executable is created, we are going to profile that code.
For the purpose of this tutorial, we use several profilers as described below:
- PGPROF - a powerful and simple analyzer for parallel programs written with OpenMP or OpenACC directives, or with CUDA.
We note that Portland Group Profiler is free for academic usage.
- NVIDIA Visual Profiler NVVP - a cross-platform analyzing tool for the codes written with OpenACC and CUDA C/C++ instructions.
- NVPROF - a command line text-based version of the NVIDIA Visual Profiler.
PGPROF Profiler
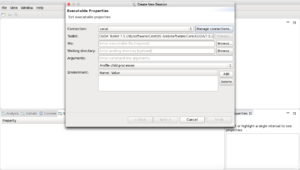
These next pictures demonstrate how to start with the PGPROF profiler. The first step is to initiate a new session. Then, browse for an executable file of the code you want to profile. Finally, specify the profiling options; for example, if you need to profile CPU activity then click the "Profile execution of the CPU" box.
NVIDIA Visual Profiler
Another profiler available for OpenACC applications is the NVIDIA Visual Profiler. It's a crossplatform analyzing tool for code written with OpenACC and CUDA C/C++ instructions.
NVIDIA NVPROF Command Line Profiler
NVIDIA also provides a command line version called NVPROF, similar to GPU prof
[name@server ~]$ nvprof --cpu-profiling on ./cg.x
<Program output >
======== CPU profiling result (bottom up):
84.25% matvec(matrix const &, vector const &, vector const &)
84.25% main
9.50% waxpby(double, vector const &, double, vector const &, vector const &)
3.37% dot(vector const &, vector const &)
2.76% allocate_3d_poisson_matrix(matrix&, int)
2.76% main
0.11% __c_mset8
0.03% munmap
0.03% free_matrix(matrix&)
0.03% main
======== Data collected at 100Hz frequency
Compiler Feedback
Before working on the routine, we need to understand what the compiler is actually doing by asking ourselves the following questions:
- What optimizations were applied?
- What prevented further optimizations?
- Can very minor modifications of the code affect performance?
The PGI compiler offers you a -Minfo flag with the following options:
- accel – Print compiler operations related to the accelerator
- all – Print all compiler output
- intensity – Print loop intensity information
- ccff–Add information to the object files for use by tools
How to Enable Compiler Feedback
- Edit the Makefile
CXX=nvc++
CXXFLAGS=-fast -Minfo=all,intensity,ccff
LDFLAGS=${CXXFLAGS}
- Rebuild
[name@server ~]$ make clean; make
nvc++ -fast -Minfo=all,intensity,ccff -c -o main.o main.cpp
initialize_vector(vector &, double):
20, include "vector.h"
36, Intensity = 0.0
Memory set idiom, loop replaced by call to __c_mset8
dot(const vector &, const vector &):
21, include "vector_functions.h"
27, Intensity = 1.00
Generated vector simd code for the loop containing reductions
FMA (fused multiply-add) instruction(s) generated
waxpby(double, const vector &, double, const vector &, const vector &):
21, include "vector_functions.h"
39, Intensity = 1.00
Loop not vectorized: data dependency
Generated vector simd code for the loop
Loop unrolled 2 times
FMA (fused multiply-add) instruction(s) generated
allocate_3d_poisson_matrix(matrix &, int):
22, include "matrix.h"
43, Intensity = 0.0
Loop not fused: different loop trip count
44, Intensity = 0.0
Loop not vectorized/parallelized: loop count too small
45, Intensity = 0.0
57, Intensity = 0.0
59, Intensity = 0.0
Loop not vectorized: data dependency
matvec(const matrix &, const vector &, const vector &):
23, include "matrix_functions.h"
29, Intensity = (num_rows*((row_end-row_start)* 2))/(num_rows+(num_rows+(num_rows+((row_end-row_start)+(row_end-row_start)))))
FMA (fused multiply-add) instruction(s) generated
33, Intensity = 1.00
Loop not vectorized: non-stride-1 array reference
Loop not vectorized: mixed data types
Loop unrolled 2 times
FMA (fused multiply-add) instruction(s) generated
main:
38, allocate_3d_poisson_matrix(matrix &, int) inlined, size=41 (inline) file main.cpp (29)
43, Intensity = 0.0
Loop not fused: different loop trip count
44, Intensity = 0.0
Loop not vectorized/parallelized: loop count too small
45, Intensity = 0.0
57, Intensity = 0.0
Loop not fused: function call before adjacent loop
59, Intensity = 0.0
Loop not vectorized: data dependency
42, allocate_vector(vector &, unsigned int) inlined, size=3 (inline) file main.cpp (24)
43, allocate_vector(vector &, unsigned int) inlined, size=3 (inline) file main.cpp (24)
44, allocate_vector(vector &, unsigned int) inlined, size=3 (inline) file main.cpp (24)
45, allocate_vector(vector &, unsigned int) inlined, size=3 (inline) file main.cpp (24)
46, allocate_vector(vector &, unsigned int) inlined, size=3 (inline) file main.cpp (24)
48, initialize_vector(vector &, double) inlined, size=5 (inline) file main.cpp (34)
36, Intensity = 0.0
Loop not vectorized/parallelized: not countable
49, initialize_vector(vector &, double) inlined, size=5 (inline) file main.cpp (34)
36, Intensity = 0.0
Loop not vectorized/parallelized: not countable
52, waxpby(double, const vector &, double, const vector &, const vector &) inlined, size=10 (inline) file main.cpp (33)
39, Intensity = 0.0
Memory copy idiom, loop replaced by call to __c_mcopy8
53, matvec(const matrix &, const vector &, const vector &) inlined, size=19 (inline) file main.cpp (20)
29, Intensity = [symbolic], and not printable, try the -Mpfi -Mpfo options
Loop not fused: different loop trip count
33, Intensity = 1.00
Loop not vectorized: non-stride-1 array reference
Loop not vectorized: mixed data types
Loop unrolled 2 times
54, waxpby(double, const vector &, double, const vector &, const vector &) inlined, size=10 (inline) file main.cpp (33)
27, FMA (fused multiply-add) instruction(s) generated
29, FMA (fused multiply-add) instruction(s) generated
33, FMA (fused multiply-add) instruction(s) generated
39, Intensity = 0.67
Loop not fused: different loop trip count
Loop not vectorized: data dependency
Generated vector simd code for the loop
Loop unrolled 4 times
FMA (fused multiply-add) instruction(s) generated
56, dot(const vector &, const vector &) inlined, size=9 (inline) file main.cpp (21)
27, Intensity = 1.00
Loop not fused: function call before adjacent loop
Generated vector simd code for the loop containing reductions
61, Intensity = 0.0
62, waxpby(double, const vector &, double, const vector &, const vector &) inlined, size=10 (inline) file main.cpp (33)
39, Intensity = 0.0
Memory copy idiom, loop replaced by call to __c_mcopy8
65, dot(const vector &, const vector &) inlined, size=9 (inline) file main.cpp (21)
27, Intensity = 1.00
Loop not fused: different loop trip count
Generated vector simd code for the loop containing reductions
67, waxpby(double, const vector &, double, const vector &, const vector &) inlined, size=10 (inline) file main.cpp (33)
39, Intensity = 0.67
Loop not fused: different loop trip count
Loop not vectorized: data dependency
Generated vector simd code for the loop
Loop unrolled 4 times
72, matvec(const matrix &, const vector &, const vector &) inlined, size=19 (inline) file main.cpp (20)
29, Intensity = [symbolic], and not printable, try the -Mpfi -Mpfo options
Loop not fused: different loop trip count
33, Intensity = 1.00
Loop not vectorized: non-stride-1 array reference
Loop not vectorized: mixed data types
Loop unrolled 2 times
73, dot(const vector &, const vector &) inlined, size=9 (inline) file main.cpp (21)
27, Intensity = 1.00
Loop not fused: different loop trip count
Generated vector simd code for the loop containing reductions
77, waxpby(double, const vector &, double, const vector &, const vector &) inlined, size=10 (inline) file main.cpp (33)
39, Intensity = 0.67
Loop not fused: different loop trip count
Loop not vectorized: data dependency
Generated vector simd code for the loop
Loop unrolled 4 times
78, waxpby(double, const vector &, double, const vector &, const vector &) inlined, size=10 (inline) file main.cpp (33)
39, Intensity = 0.67
Loop not fused: function call before adjacent loop
Loop not vectorized: data dependency
Generated vector simd code for the loop
Loop unrolled 4 times
88, free_vector(vector &) inlined, size=2 (inline) file main.cpp (29)
89, free_vector(vector &) inlined, size=2 (inline) file main.cpp (29)
90, free_vector(vector &) inlined, size=2 (inline) file main.cpp (29)
91, free_vector(vector &) inlined, size=2 (inline) file main.cpp (29)
92, free_matrix(matrix &) inlined, size=5 (inline) file main.cpp (73)
nvc++ main.o -o cg.x -fast -Minfo=all,intensity,ccff
Computational Intensity
Computational Intensity of a loop is a measure of how much work is being done compared to memory operations.
Computation Intensity = Compute Operations / Memory Operations
Computational Intensity of 1.0 or greater suggests that the loop might run well on a GPU.
Understanding the code
Let's look closely at the following code from matrix_functions.h:
for(int i=0;i<num_rows;i++) {
double sum=0;
int row_start=row_offsets[i];
int row_end=row_offsets[i+1];
for(int j=row_start; j<row_end;j++) {
unsigned int Acol=cols[j];
double Acoef=Acoefs[j];
double xcoef=xcoefs[Acol];
sum+=Acoef*xcoef;
}
ycoefs[i]=sum;
}
Given the code above, we search for data dependencies:
- Does one loop iteration affect other loop iterations?
- Do loop iterations read from and write to different places in the same array?
- Is sum a data dependency? No, it’s a reduction.
Now that the code analysis is done, we are ready to add directives to the compiler.
<- Previous unit: Introduction | ^- Back to the lesson plan | Onward to the next unit: Adding directives ->