Vtune/fr: Difference between revisions
(Diane27) |
(Created page with "# Connectez-vous à gra-vid avec [https://docs.computecanada.ca/wiki/VNC/fr#Noeuds_VDI TigerVNC];[https://docs.computecanada.ca/wiki/VNC#VDI_Nodes TigerVNC] # <code>module lo...") |
||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
== Nœuds VDI == | == Nœuds VDI == | ||
# | # Connectez-vous à gra-vid avec [https://docs.computecanada.ca/wiki/VNC/fr#Noeuds_VDI TigerVNC];[https://docs.computecanada.ca/wiki/VNC#VDI_Nodes TigerVNC] | ||
# <code>module load CcEnv StdEnv/2016.4 *OR* StdEnv/2018.3</code> | # <code>module load CcEnv StdEnv/2016.4 *OR* StdEnv/2018.3</code> | ||
# <code>module load intel/2019.3</code> (optional) | # <code>module load intel/2019.3</code> (optional) | ||
Revision as of 17:58, 28 July 2021
Introduction
VTune est un produit d'Intel pour analyser la performance des systèmes et des applications OpenMP et MPI.
Module logiciel
Pour charger le module sur une de nos grappes, lancez
[name@server ~]$ module load vtune
Nom du produit
The content of this page is largely concerned with the legacy version named Intel® VTune™ Amplifier. Please note this tool has been renamed throughout Intel's documentation in latest versions (newer than the latest vtune module versions presently available on Compute Canada clusters) from Intel® VTune™ Amplifier to Intel® VTune™ Profiler. Likewise the application commands amplxe-cl and amplxe-gui have been renamed to vtune and vtune-gui for both the command line and graphical tools respectively. Once a version with the newer naming convention is available as a loadable module in the forthcoming default StdEnv/2020 environment this Wiki page will be updated accordingly. Further information can be found here.
Collect analysis
To collect analysis information run:
[name@server ~]$ amplxe-cl -collect <analysis-type> <target_exe> <exe_arguments>
where <analysis-type> should be replaced by one of the available analysis, e.g. hotspots, and <target_exe> is the path to the executable you would like to analyze. It is recommended to compile your executable with the "-g" option and to use the same optimization level as normal so as to obtain accurate results. A listing of version specific argument options and several usage examples maybe displayed on the command line by running amplxe-cl -help, after loading the vtune module. Complete downloadable documentation for Parallel Studio XE (including VTune) for all recent versions can be found here. The latest version of the Intel VTune Profiler User Guide may be found here.
Créer un rapport
Pour créer un rapport, lancez
[name@server ~]$ amplxe-cl -report <report-type>
où <report-type> est le type de rapport à générer (hotspots). Voyez aussi la page Generate Command Line Reports.
Exemple de matrice
Analyze and generate a summary report for the Intel Matrix Sample Project run from the command line with 4 cores:
salloc --time=1:00:00 --cpus-per-task=4 --ntasks=1 --mem=16G --account=def-yours module load StdEnv/2016.4 *OR* StdEnv/2018.3 module load intel/2019.3 (optional) module load vtune/2019.3 cp -a $EBROOTVTUNE/vtune_amplifier/samples/en/C++/matrix . cd matrix/linux make icc amplxe-cl -collect hotspots ../matrix amplxe-cl -report summary
La plus récente version de matrix_multiply (qui construit avec cmake) se trouve ici.
Mode graphique
The Intel Matrix Sample Project an also be run using Vtune in GUI mode as explored here [1]. To run VTune over VNC follow the below directions depending on which system you wish to use. Running VTune graphically can be useful to generate command line configurations as discussed in [2].
Nœuds des grappes
- Connectez-vous à un nœud de calcul ou à un nœud de connexion avec TigerVNC;
module load StdEnv/2016.4 *OR* StdEnv/2018.3module load intel/2019.3(optional)module load vtune/2019.3amplxe-gui
Nœuds VDI
- Connectez-vous à gra-vid avec TigerVNC;TigerVNC
module load CcEnv StdEnv/2016.4 *OR* StdEnv/2018.3module load intel/2019.3(optional)module load vtune/2019.3amplxe-gui
MPI example
First, load the latest VTune module.
module load StdEnv/2020 module load vtune
Then compile your MPI program as you usually would and run it inside a job or in an interactive session started by a salloc command using:
srun aps your_mpi_program.x
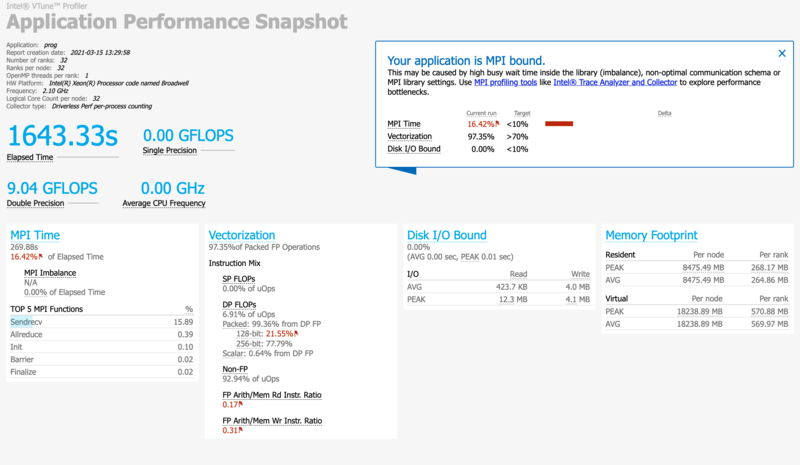
After the program finishes, the profiling data will be stored in a directory called aps_result_YYYYMMDD where YYYYMMDD is the current date.
There is a lot of information you can extract from that data. To get the basic summary report of your program's performance, run:
aps-report -D aps_result_YYYYMMDD
where you would replace YYYYMMDD to match the actual directory that has been created. This command creates an HTML file, which can be copied to your own computer and viewed in a browser. The report will clearly identify performance issues that are affecting your code.