Vtune/fr: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "Vtune") |
No edit summary |
||
| (44 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
= Introduction = | = Introduction = | ||
[https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/tools/oneapi/components/vtune-profiler.html VTune] | [https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/tools/oneapi/components/vtune-profiler.html VTune] est un produit d'Intel pour analyser la performance des systèmes et des applications [https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/documentation/itac-vtune-mpi-openmp-tutorial-lin/top.html OpenMP et MPI]. | ||
= | = Module logiciel= | ||
Pour charger le module sur une de nos grappes, lancez | |||
{{Command|module load vtune}} | {{Command|module load vtune}} | ||
= | = Changement de noms = | ||
Il sera question ici de Intel® VTune™ Amplifier, dont le nom a été changé pour Intel® VTune™ Profiler dans la documentation des plus récentes versions. Aussi, les commandes <tt>amplxe-cl</tt> et <tt>amplxe-gui</tt> ont été renommées <tt>vtune</tt> et <tt>vtune-gui</tt> respectivement pour la ligne de commande et les outils graphiques. Les versions des modules VTune offertes pour nos grappes sont antérieures au changement de ces noms. Pour plus d'information, voyez [https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/documentation/vtune-help/top/launch.html cette page du guide de l'utilisateur]. | |||
= | = Types d'analyses = | ||
Pour collecter de l'information pour analyse, lancez | |||
{{Command| | {{Command|vtune -collect <analysis-type> <target_exe> <exe_arguments>}} | ||
où <analysis-type> est le nom d'un type d'analyse disponible (par ex. ''hotspots''), et <target_exe> est le chemin vers l'exécutable que vous voulez analyser. Nous vous recommandons de compiler votre exécutable avec l'option <tt>-g</tt> et d'utiliser le niveau d'optimisation normal afin d'obtenir des résultats exacts. Il est possible de faire lister sur la ligne de commande des options d'arguments spécifiques à une version ainsi que plusieurs exemples d'utilisation avec <code>vtune -help</code>, après avoir chargé le module VTune. | |||
Téléchargez [https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/articles/download-documentation-intel-parallel-studio-xe-current-previous.html la documentation de Parallel Studio XE (incluant VTune)] et le [https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/documentation/vtune-help/top.html guide de l'utilisateur Intel VTune Profiler User Guide]. | |||
= | = Créer un rapport = | ||
Pour créer un rapport, lancez | |||
{{Command| | {{Command|vtune -report <report-type> }} | ||
où <report-type> est le type de rapport à générer (''hotspots''). Voyez aussi la page [https://software.intel.com/en-us/vtune-amplifier-help-generating-command-line-reports Generate Command Line Reports]. | |||
= | = Exemple de matrice = | ||
Pour analyser et générer le projet Intel ''Matrix Sample Project'' en ligne de commande avec 4 cœurs : | |||
salloc --time=1:00:00 --cpus-per-task=4 --ntasks=1 --mem=16G --account=def-yours | salloc --time=1:00:00 --cpus-per-task=4 --ntasks=1 --mem=16G --account=def-yours | ||
module load StdEnv/ | module load StdEnv/2020 vtune | ||
cp -a $EBROOTVTUNE/vtune/$EBVERSIONVTUNE*/samples/en/C++/matrix . cd matrix/linux | |||
cp -a $EBROOTVTUNE/ | |||
make icc | make icc | ||
vtune -collect hotspots ../matrix | |||
vtune -report summary | |||
La plus récente version de matrix_multiply (qui construit avec <tt>cmake</tt>) [https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneAPI-samples/tree/master/Tools/VTuneProfiler se trouve ici]. | |||
= | = Mode graphique = | ||
Intel Matrix Sample Project peut être exécuté en mode graphique, comme décrit ici [https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/documentation/vtune-hotspots-tutorial-linux-c/top/run-hotspots-analysis.html]. Pour utiliser VTune dans VNC voyez les directives ci-dessous. Le mode graphique peut être utile pour générer des configurations en commande de ligne, comme décrit ici [https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/documentation/vtune-help/top/analyze-performance/control-data-collection/generating-command-line-configuration-from-gui.html]. | |||
== | == Nœuds des grappes == | ||
# | # Connectez-vous à un nœud de calcul ou à un nœud de connexion avec [https://docs.alliancecan.ca/wiki/VNC/fr#Connexion TigerVNC]; | ||
# <code>module load StdEnv/ | # <code>module load StdEnv/2020 vtune</code> | ||
# <code> | # <code>vtune-gui</code><br> | ||
== VDI | == Nœuds VDI == | ||
# | # Connectez-vous à un nœud de calcul ou à un nœud de connexion avec [https://docs.alliancecan.ca/wiki/VNC/fr#Connexion TigerVNC]; | ||
# <code>module load CcEnv StdEnv/ | # <code>module load CcEnv StdEnv/2020 vtune</code> | ||
# <code> | # <code>vtune-gui</code><br> | ||
Latest revision as of 21:09, 20 February 2024
Introduction
VTune est un produit d'Intel pour analyser la performance des systèmes et des applications OpenMP et MPI.
Module logiciel
Pour charger le module sur une de nos grappes, lancez
[name@server ~]$ module load vtune
Changement de noms
Il sera question ici de Intel® VTune™ Amplifier, dont le nom a été changé pour Intel® VTune™ Profiler dans la documentation des plus récentes versions. Aussi, les commandes amplxe-cl et amplxe-gui ont été renommées vtune et vtune-gui respectivement pour la ligne de commande et les outils graphiques. Les versions des modules VTune offertes pour nos grappes sont antérieures au changement de ces noms. Pour plus d'information, voyez cette page du guide de l'utilisateur.
Types d'analyses
Pour collecter de l'information pour analyse, lancez
[name@server ~]$ vtune -collect <analysis-type> <target_exe> <exe_arguments>
où <analysis-type> est le nom d'un type d'analyse disponible (par ex. hotspots), et <target_exe> est le chemin vers l'exécutable que vous voulez analyser. Nous vous recommandons de compiler votre exécutable avec l'option -g et d'utiliser le niveau d'optimisation normal afin d'obtenir des résultats exacts. Il est possible de faire lister sur la ligne de commande des options d'arguments spécifiques à une version ainsi que plusieurs exemples d'utilisation avec vtune -help, après avoir chargé le module VTune.
Téléchargez la documentation de Parallel Studio XE (incluant VTune) et le guide de l'utilisateur Intel VTune Profiler User Guide.
Créer un rapport
Pour créer un rapport, lancez
[name@server ~]$ vtune -report <report-type>
où <report-type> est le type de rapport à générer (hotspots). Voyez aussi la page Generate Command Line Reports.
Exemple de matrice
Pour analyser et générer le projet Intel Matrix Sample Project en ligne de commande avec 4 cœurs :
salloc --time=1:00:00 --cpus-per-task=4 --ntasks=1 --mem=16G --account=def-yours module load StdEnv/2020 vtune cp -a $EBROOTVTUNE/vtune/$EBVERSIONVTUNE*/samples/en/C++/matrix . cd matrix/linux make icc vtune -collect hotspots ../matrix vtune -report summary
La plus récente version de matrix_multiply (qui construit avec cmake) se trouve ici.
Mode graphique
Intel Matrix Sample Project peut être exécuté en mode graphique, comme décrit ici [1]. Pour utiliser VTune dans VNC voyez les directives ci-dessous. Le mode graphique peut être utile pour générer des configurations en commande de ligne, comme décrit ici [2].
Nœuds des grappes
- Connectez-vous à un nœud de calcul ou à un nœud de connexion avec TigerVNC;
module load StdEnv/2020 vtunevtune-gui
Nœuds VDI
- Connectez-vous à un nœud de calcul ou à un nœud de connexion avec TigerVNC;
module load CcEnv StdEnv/2020 vtunevtune-gui
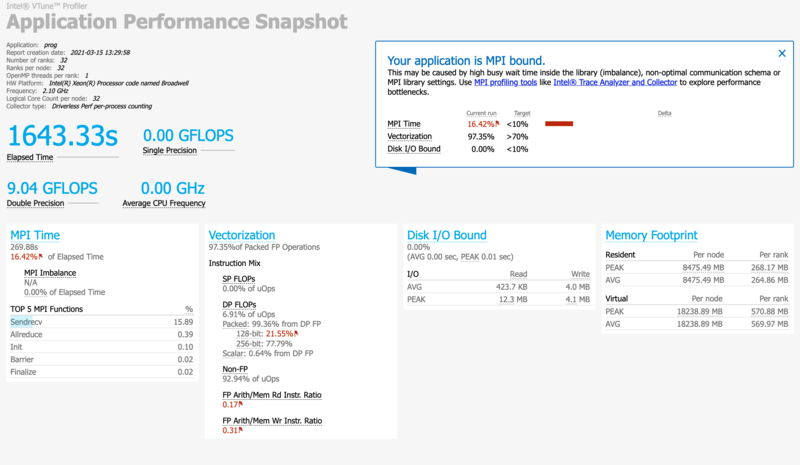
MPI example
First, load the latest VTune module.
module load StdEnv/2020 module load vtune
Then compile your MPI program as you usually would and run it inside a job or in an interactive session started by a salloc command using:
srun aps your_mpi_program.x
After the program finishes, the profiling data will be stored in a directory called aps_result_YYYYMMDD where YYYYMMDD is the current date.
There is a lot of information you can extract from that data. To get the basic summary report of your program's performance, run:
aps-report -D aps_result_YYYYMMDD
where you would replace YYYYMMDD to match the actual directory that has been created. This command creates an HTML file, which can be copied to your own computer and viewed in a browser. The report will clearly identify performance issues that are affecting your code.