CephFS: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(Marked this version for translation) |
||
| (54 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
If you do not already have a quota for the service, you will need to request this through [mailto:cloud@tech.alliancecan.ca cloud@tech.alliancecan.ca]. In your request please provide the following: | If you do not already have a quota for the service, you will need to request this through [mailto:cloud@tech.alliancecan.ca cloud@tech.alliancecan.ca]. In your request please provide the following: | ||
* OpenStack project name | * OpenStack project name | ||
* amount of quota required in GB | * amount of quota required (in GB) | ||
* number of shares required | * number of shares required | ||
== | == OpenStack configuration: Create a CephFS share == <!--T:6--> | ||
<!--T:7--> | <!--T:7--> | ||
; Create the share. | |||
: In <i>Project --> Share --> Shares</i>, click on <i>+Create Share</i>. | |||
: <i>Share Name</i> = enter a name that identifies your project (e.g. <i>project-name-shareName</i>) | |||
: <i>Share Protocol</i> = CephFS | |||
: <i>Size</i> = size you need for this share | |||
: <i>Share Type</i> = cephfs | |||
: <i>Availability Zone</i> = nova | |||
: Do not check <i>Make visible for all</i>, otherwise the share will be accessible by all users in all projects. | |||
: Click on the <i>Create</i> button. | |||
[[File:Cephfs config.png|450px|thumb|left|Configuration of CephFS on Horizon GUI]] | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
= | <!--T:20--> | ||
; Create an access rule to generate access key. | |||
: In <i>Project --> Share --> Shares --> Actions</i> column, select <i>Manage Rules</i> from the drop-down menu. | |||
: Click on the <i>+Add Rule</i> button (right of the page). | |||
: <i>Access Type</i> = cephx | |||
: <i>Access Level</i> = select <i>read-write</i> or <i>read-only</i> (you can create multiple rules for either access level if required) | |||
: <i>Access To</i> = select a key name that describes the key. This name is important because it will be used in the cephfs client configuration on the VM; on this page, we use <i>MyCephFS-RW</i>. | |||
[[File:Cephfs created.png|450px|thumb|left||Properly configured CephFS]] | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
< | <!--T:21--> | ||
< | ; Note the share details which you will need later. | ||
< | : In <i>Project --> Share --> Shares</i>, click on the name of the share. | ||
< | : In the <i>Share Overview</i>, note the three elements circled in red in the "Properly configured" image: <i>Path</i>, which will be used in the mount command on the VM, the <i>Access Rules</i>, which will be the client name and the <i>Access Key</i> that will let the VM's client connect. | ||
< | |||
== Attach the CephFS network to your VM == <!--T:8--> | |||
< | === On Arbutus === <!--T:22--> | ||
On <code>Arbutus</code>, the cephFS network is already exposed to your VM; there is nothing to do here, '''[[CephFS#VM_configuration:_install_and_configure_CephFS_client|go to the VM configuration section]]'''. | |||
=== On SD4H/Juno === <!--T:23--> | |||
On <code>SD4H/Juno</code>, you need to explicitly attach the cephFS network to the VM. | |||
<!--T:24--> | |||
;With the Web Gui | |||
For each VM you need to attach, select <i>Instance --> Action --> Attach interface</i> select the CephFS-Network, leave the <i>Fixed IP Address</i> box empty. | |||
[[File:Select CephFS Network.png|750px|thumb|left|]] | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
;With the [[OpenStack_command_line_clients|Openstack client]] | |||
List the servers and select the id of the server you need to attach to the CephFS | |||
<source lang='bash'> | |||
$ openstack server list | |||
+--------------------------------------+--------------+--------+-------------------------------------------+--------------------------+----------+ | |||
| ID | Name | Status | Networks | Image | Flavor | | |||
+--------------------------------------+--------------+--------+-------------------------------------------+--------------------------+----------+ | |||
| 1b2a3c21-c1b4-42b8-9016-d96fc8406e04 | prune-dtn1 | ACTIVE | test_network=172.16.1.86, 198.168.189.3 | N/A (booted from volume) | ha4-15gb | | |||
| 0c6df8ea-9d6a-43a9-8f8b-85eb64ca882b | prune-mgmt1 | ACTIVE | test_network=172.16.1.64 | N/A (booted from volume) | ha4-15gb | | |||
| 2b7ebdfa-ee58-4919-bd12-647a382ec9f6 | prune-login1 | ACTIVE | test_network=172.16.1.111, 198.168.189.82 | N/A (booted from volume) | ha4-15gb | | |||
+--------------------------------------+--------------+--------+----------------------------------------------+--------------------------+----------+ | |||
</source> | |||
<!--T:25--> | |||
Select the ID of the VM you want to attach, will pick the first one here and run | |||
<source lang='bash'> | |||
$ openstack server add network 1b2a3c21-c1b4-42b8-9016-d96fc8406e04 CephFS-Network | |||
$ openstack server list | |||
+--------------------------------------+--------------+--------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------------------+----------+ | |||
| ID | Name | Status | Networks | Image | Flavor | | |||
+--------------------------------------+--------------+--------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------------------+----------+ | |||
| 1b2a3c21-c1b4-42b8-9016-d96fc8406e04 | prune-dtn1 | ACTIVE | CephFS-Network=10.65.20.71; test_network=172.16.1.86, 198.168.189.3 | N/A (booted from volume) | ha4-15gb | | |||
| 0c6df8ea-9d6a-43a9-8f8b-85eb64ca882b | prune-mgmt1 | ACTIVE | test_network=172.16.1.64 | N/A (booted from volume) | ha4-15gb | | |||
| 2b7ebdfa-ee58-4919-bd12-647a382ec9f6 | prune-login1 | ACTIVE | test_network=172.16.1.111, 198.168.189.82 | N/A (booted from volume) | ha4-15gb | | |||
+--------------------------------------+--------------+--------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------------------+----------+ | |||
</source> | |||
<!--T:26--> | |||
We can see that the CephFS network is attached to the first VM. | |||
== VM configuration: install and configure CephFS client == <!--T:9--> | |||
=== Required packages for the Red Hat family (RHEL, CentOS, Fedora, Rocky, Alma ) === <!--T:27--> | |||
Check the available releases at [https://download.ceph.com/ https://download.ceph.com/] and look for recent <code>rpm-*</code> directories. | |||
As of July 2024, <code>quincy</code> is the latest stable release. | |||
The compatible distributions (distros) are listed at [https://download.ceph.com/rpm-quincy/ https://download.ceph.com/rpm-quincy/]. | |||
Here we show configuration examples for <code>Enterprise Linux 8</code> and <code>Enterprise Linux 9</code>. | |||
<!--T:28--> | |||
; Install relevant repositories for access to ceph client packages: | |||
<!--T:29--> | |||
<tabs> | |||
<tab name="Enterprise Linux 8 - el8"> | |||
{{File | {{File | ||
|name=/etc/yum.repos.d/ceph.repo | |name=/etc/yum.repos.d/ceph.repo | ||
| Line 70: | Line 118: | ||
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc | gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc | ||
<!--T:51--> | |||
[Ceph-noarch] | [Ceph-noarch] | ||
name=Ceph noarch packages | name=Ceph noarch packages | ||
| Line 78: | Line 127: | ||
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc | gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc | ||
<!--T:52--> | |||
[ceph-source] | [ceph-source] | ||
name=Ceph source packages | name=Ceph source packages | ||
| Line 86: | Line 136: | ||
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc | gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc | ||
}} | }} | ||
</tab> | |||
<tab name="Enterprise Linux 9 - el9"> | |||
{{File | |||
|name=/etc/yum.repos.d/ceph.repo | |||
|lang="ini" | |||
|contents= | |||
[Ceph] | |||
name=Ceph packages for $basearch | |||
baseurl=http://download.ceph.com/rpm-quincy/el9/$basearch | |||
enabled=1 | |||
gpgcheck=1 | |||
type=rpm-md | |||
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc | |||
<!--T:53--> | |||
[Ceph-noarch] | |||
name=Ceph noarch packages | |||
baseurl=http://download.ceph.com/rpm-quincy/el9/noarch | |||
enabled=1 | |||
gpgcheck=1 | |||
type=rpm-md | |||
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc | |||
<!--T:54--> | |||
[ceph-source] | |||
name=Ceph source packages | |||
baseurl=http://download.ceph.com/rpm-quincy/el9/SRPMS | |||
enabled=1 | |||
gpgcheck=1 | |||
type=rpm-md | |||
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc | |||
}} | |||
</tab> | |||
</tabs> | |||
The epel repo also | <!--T:32--> | ||
The epel repo also needs to be in place | |||
sudo dnf install epel-release | sudo dnf install epel-release | ||
You can now install the ceph lib, cephfs client and other | <!--T:33--> | ||
You can now install the ceph lib, cephfs client and other dependencies: | |||
sudo dnf install -y libcephfs2 python3-cephfs ceph-common python3-ceph-argparse | sudo dnf install -y libcephfs2 python3-cephfs ceph-common python3-ceph-argparse | ||
=== Required packages for the Debian family (Debian, Ubuntu, Mint, etc.) === <!--T:34--> | |||
You can get the repository once you have figured out your distro <code>{codename}</code> with <code>lsb_release -sc</code> | |||
You can get the repository | <source lang='bash'> | ||
sudo apt-add-repository 'deb https://download.ceph.com/debian-quincy/ {codename} main' | |||
</source> | |||
< | <!--T:50--> | ||
You can now install the ceph lib, cephfs client and other dependencies: | |||
< | <source lang='bash'> | ||
sudo apt-get install -y libcephfs2 python3-cephfs ceph-common python3-ceph-argparse | |||
</source> | |||
=== Configure ceph client === <!--T:35--> | |||
<!--T:36--> | |||
Once the client is installed, you can create a <code>ceph.conf</code> file. | |||
Note the different <code>mon host</code> for the different cloud. | |||
<tabs> | <tabs> | ||
<tab name="Arbutus"> | <tab name="Arbutus"> | ||
| Line 110: | Line 203: | ||
|lang="ini" | |lang="ini" | ||
|contents= | |contents= | ||
[global] | |||
admin socket = /var/run/ceph/$cluster-$name-$pid.asok | |||
client reconnect stale = true | |||
debug client = 0/2 | |||
fuse big writes = true | |||
mon host = 10.30.201.3:6789,10.30.202.3:6789,10.30.203.3:6789 | |||
[client] | [client] | ||
quota = true | |||
}} | }} | ||
</tab> | </tab> | ||
| Line 132: | Line 230: | ||
</tabs> | </tabs> | ||
<!--T:37--> | |||
You can find the monitor information in the share details <i>Path</i> field that will be used to mount the volume. If the value of the web page is different than what is seen here, it means that the wiki page is out of date. | |||
<!--T:38--> | |||
You also need to put your client name and secret in the <code>ceph.keyring</code> file | |||
<!--T:39--> | |||
{{File | |||
|name=/etc/ceph/ceph.keyring | |||
|lang="ini" | |||
|contents= | |||
[client.MyCephFS-RW] | |||
key = <access Key> | |||
}} | |||
<!--T:40--> | |||
Again, the access key and client name (here MyCephFS-RW) are found under the access rules on your project web page. | |||
Look for <i>Project --> Share --> Shares</i>, then click on the name of the share. | |||
<!--T:41--> | |||
; Retrieve the connection information from the share page for your connection: | |||
: Open up the share details by clicking on the name of the share in the <i>Shares</i> page. | |||
: Copy the entire path of the share to mount the filesystem. | |||
<!--T:42--> | |||
;Mount the filesystem | |||
:Create a mount point directory somewhere in your host (<code>/cephfs</code>, is used here)</li> | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
mkdir /cephfs | |||
</source> | |||
:You can use the ceph driver to permanently mount your CephFS device by adding the following in the VM fstab | |||
<tabs> | |||
<tab name="Arbutus"> | |||
{{File | |||
|name=/etc/fstab | |||
|lang="txt" | |||
|contents= | |||
:/volumes/_nogroup/f6cb8f06-f0a4-4b88-b261-f8bd6b03582c /cephfs/ ceph name=MyCephFS-RW 0 2 | |||
}} | |||
</tab> | |||
<tab name="SD4H/Juno"> | |||
{{File | |||
|name=/etc/fstab | |||
|lang="txt" | |||
|contents= | |||
:/volumes/_nogroup/f6cb8f06-f0a4-4b88-b261-f8bd6b03582c /cephfs/ ceph name=MyCephFS-RW,mds_namespace=cephfs_4_2,x-systemd.device-timeout=30,x-systemd.mount-timeout=30,noatime,_netdev,rw 0 2 | |||
}} | |||
</tab> | |||
</tabs> | |||
<!--T:43--> | |||
'''Notice''' the non-standard <code>:</code> before the device path. It is not a typo! | |||
The mount options are different on different systems. | |||
The namespace option is required for SD4H/Juno, while other options are performance tweaks. | |||
<!--T:44--> | |||
You can also do the mount directly from the command line: | |||
<tabs> | |||
<tab name="Arbutus"> | |||
<code> | |||
sudo mount -t ceph :/volumes/_nogroup/f6cb8f06-f0a4-4b88-b261-f8bd6b03582c /cephfs/ -o name=MyCephFS-RW | |||
</code> | |||
</tab> | |||
<tab name="SD4H/Juno"> | |||
<code> | |||
sudo mount -t ceph :/volumes/_nogroup/f6cb8f06-f0a4-4b88-b261-f8bd6b03582c /cephfs/ -o name=MyCephFS-RW,mds_namespace=cephfs_4_2,x-systemd.device-timeout=30,x-systemd.mount-timeout=30,noatime,_netdev,rw | |||
</code> | |||
</tab> | |||
</tabs> | |||
<!--T:45--> | |||
CephFS is can also be mounted directly in user space via ceph-fuse. | |||
<!--T:46--> | |||
Install the ceph-fuse lib | |||
<!--T:47--> | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
sudo dnf install ceph-fuse | |||
</source> | |||
Let the fuse mount be accessible in userspace by uncommenting <code>user_allow_other</code> in the <code>fuse.conf</code> file. | |||
<!--T:48--> | |||
{{File | |||
|name=/etc/fuse.conf | |||
|lang="txt" | |||
|contents= | |||
# mount_max = 1000 | |||
user_allow_other | |||
}} | |||
< | <!--T:49--> | ||
You can now mount cephFS in a user’s home: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | |||
mkdir ~/my_cephfs | |||
ceph-fuse my_cephfs/ --id=MyCephFS-RW --conf=~/ceph.conf --keyring=~/ceph.keyring --client-mountpoint=/volumes/_nogroup/f6cb8f06-f0a4-4b88-b261-f8bd6b03582c | |||
</source> | |||
Note that the client name is here the <code>--id</code>. The <code>ceph.conf</code> and <code>ceph.keyring</code> content are exactly the same as for the ceph kernel mount. | |||
< | |||
< | |||
< | |||
< | |||
=Notes= <!--T: | =Notes= <!--T:10--> | ||
<!--T: | <!--T:11--> | ||
A particular share can have more than one user key provisioned for it. This allows a more granular access to the filesystem, for example, if you needed some hosts to only access the filesystem in a read-only capacity. If you have multiple keys for a share, you can add the extra keys to your host and modify the above mounting procedure. This service is not available to hosts outside of the OpenStack cluster. | |||
<!--T: | <!--T:12--> | ||
[[Category:Cloud]] | [[Category:Cloud]] | ||
</translate> | </translate> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:59, 16 October 2024
CephFS provides a common filesystem that can be shared amongst multiple OpenStack VM hosts. Access to the service is granted via requests to cloud@tech.alliancecan.ca.
This is a fairly technical procedure that assumes basic Linux skills for creating/editing files, setting permissions, and creating mount points. For assistance in setting up this service, write to cloud@tech.alliancecan.ca.
Procedure
If you do not already have a quota for the service, you will need to request this through cloud@tech.alliancecan.ca. In your request please provide the following:
- OpenStack project name
- amount of quota required (in GB)
- number of shares required
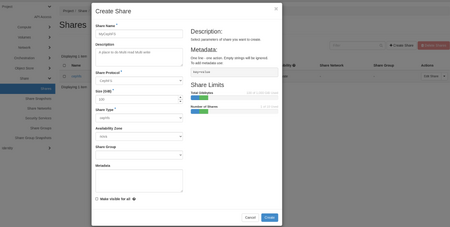
- Create the share.
- In Project --> Share --> Shares, click on +Create Share.
- Share Name = enter a name that identifies your project (e.g. project-name-shareName)
- Share Protocol = CephFS
- Size = size you need for this share
- Share Type = cephfs
- Availability Zone = nova
- Do not check Make visible for all, otherwise the share will be accessible by all users in all projects.
- Click on the Create button.
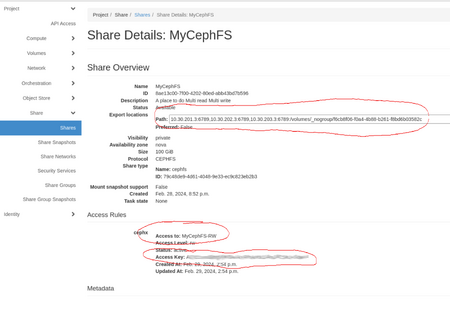
- Create an access rule to generate access key.
- In Project --> Share --> Shares --> Actions column, select Manage Rules from the drop-down menu.
- Click on the +Add Rule button (right of the page).
- Access Type = cephx
- Access Level = select read-write or read-only (you can create multiple rules for either access level if required)
- Access To = select a key name that describes the key. This name is important because it will be used in the cephfs client configuration on the VM; on this page, we use MyCephFS-RW.
- Note the share details which you will need later.
- In Project --> Share --> Shares, click on the name of the share.
- In the Share Overview, note the three elements circled in red in the "Properly configured" image: Path, which will be used in the mount command on the VM, the Access Rules, which will be the client name and the Access Key that will let the VM's client connect.
Attach the CephFS network to your VM
On Arbutus
On Arbutus, the cephFS network is already exposed to your VM; there is nothing to do here, go to the VM configuration section.
On SD4H/Juno
On SD4H/Juno, you need to explicitly attach the cephFS network to the VM.
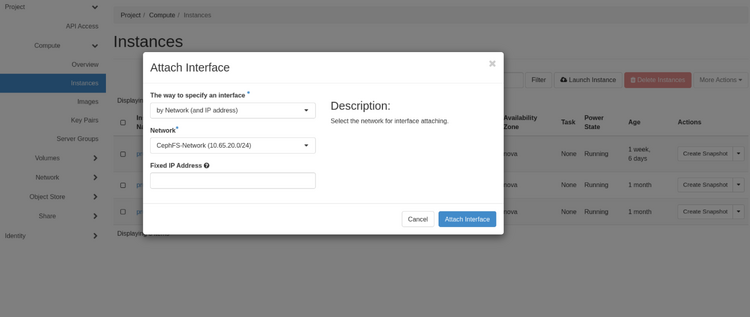
- With the Web Gui
For each VM you need to attach, select Instance --> Action --> Attach interface select the CephFS-Network, leave the Fixed IP Address box empty.
- With the Openstack client
List the servers and select the id of the server you need to attach to the CephFS
$ openstack server list
+--------------------------------------+--------------+--------+-------------------------------------------+--------------------------+----------+
| ID | Name | Status | Networks | Image | Flavor |
+--------------------------------------+--------------+--------+-------------------------------------------+--------------------------+----------+
| 1b2a3c21-c1b4-42b8-9016-d96fc8406e04 | prune-dtn1 | ACTIVE | test_network=172.16.1.86, 198.168.189.3 | N/A (booted from volume) | ha4-15gb |
| 0c6df8ea-9d6a-43a9-8f8b-85eb64ca882b | prune-mgmt1 | ACTIVE | test_network=172.16.1.64 | N/A (booted from volume) | ha4-15gb |
| 2b7ebdfa-ee58-4919-bd12-647a382ec9f6 | prune-login1 | ACTIVE | test_network=172.16.1.111, 198.168.189.82 | N/A (booted from volume) | ha4-15gb |
+--------------------------------------+--------------+--------+----------------------------------------------+--------------------------+----------+
Select the ID of the VM you want to attach, will pick the first one here and run
$ openstack server add network 1b2a3c21-c1b4-42b8-9016-d96fc8406e04 CephFS-Network
$ openstack server list
+--------------------------------------+--------------+--------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------------------+----------+
| ID | Name | Status | Networks | Image | Flavor |
+--------------------------------------+--------------+--------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------------------+----------+
| 1b2a3c21-c1b4-42b8-9016-d96fc8406e04 | prune-dtn1 | ACTIVE | CephFS-Network=10.65.20.71; test_network=172.16.1.86, 198.168.189.3 | N/A (booted from volume) | ha4-15gb |
| 0c6df8ea-9d6a-43a9-8f8b-85eb64ca882b | prune-mgmt1 | ACTIVE | test_network=172.16.1.64 | N/A (booted from volume) | ha4-15gb |
| 2b7ebdfa-ee58-4919-bd12-647a382ec9f6 | prune-login1 | ACTIVE | test_network=172.16.1.111, 198.168.189.82 | N/A (booted from volume) | ha4-15gb |
+--------------------------------------+--------------+--------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------------------+----------+
We can see that the CephFS network is attached to the first VM.
VM configuration: install and configure CephFS client
Required packages for the Red Hat family (RHEL, CentOS, Fedora, Rocky, Alma )
Check the available releases at https://download.ceph.com/ and look for recent rpm-* directories.
As of July 2024, quincy is the latest stable release.
The compatible distributions (distros) are listed at https://download.ceph.com/rpm-quincy/.
Here we show configuration examples for Enterprise Linux 8 and Enterprise Linux 9.
- Install relevant repositories for access to ceph client packages
[Ceph]
name=Ceph packages for $basearch
baseurl=http://download.ceph.com/rpm-quincy/el8/$basearch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
type=rpm-md
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc
[Ceph-noarch]
name=Ceph noarch packages
baseurl=http://download.ceph.com/rpm-quincy/el8/noarch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
type=rpm-md
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc
[ceph-source]
name=Ceph source packages
baseurl=http://download.ceph.com/rpm-quincy/el8/SRPMS
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
type=rpm-md
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc
[Ceph]
name=Ceph packages for $basearch
baseurl=http://download.ceph.com/rpm-quincy/el9/$basearch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
type=rpm-md
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc
[Ceph-noarch]
name=Ceph noarch packages
baseurl=http://download.ceph.com/rpm-quincy/el9/noarch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
type=rpm-md
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc
[ceph-source]
name=Ceph source packages
baseurl=http://download.ceph.com/rpm-quincy/el9/SRPMS
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
type=rpm-md
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc
The epel repo also needs to be in place
sudo dnf install epel-release
You can now install the ceph lib, cephfs client and other dependencies:
sudo dnf install -y libcephfs2 python3-cephfs ceph-common python3-ceph-argparse
Required packages for the Debian family (Debian, Ubuntu, Mint, etc.)
You can get the repository once you have figured out your distro {codename} with lsb_release -sc
sudo apt-add-repository 'deb https://download.ceph.com/debian-quincy/ {codename} main'
You can now install the ceph lib, cephfs client and other dependencies:
sudo apt-get install -y libcephfs2 python3-cephfs ceph-common python3-ceph-argparse
Configure ceph client
Once the client is installed, you can create a ceph.conf file.
Note the different mon host for the different cloud.
[global]
admin socket = /var/run/ceph/$cluster-$name-$pid.asok
client reconnect stale = true
debug client = 0/2
fuse big writes = true
mon host = 10.30.201.3:6789,10.30.202.3:6789,10.30.203.3:6789
[client]
quota = true
[global]
admin socket = /var/run/ceph/$cluster-$name-$pid.asok
client reconnect stale = true
debug client = 0/2
fuse big writes = true
mon host = 10.65.0.10:6789,10.65.0.12:6789,10.65.0.11:6789
[client]
quota = true
You can find the monitor information in the share details Path field that will be used to mount the volume. If the value of the web page is different than what is seen here, it means that the wiki page is out of date.
You also need to put your client name and secret in the ceph.keyring file
[client.MyCephFS-RW]
key = <access Key>
Again, the access key and client name (here MyCephFS-RW) are found under the access rules on your project web page. Look for Project --> Share --> Shares, then click on the name of the share.
- Retrieve the connection information from the share page for your connection
- Open up the share details by clicking on the name of the share in the Shares page.
- Copy the entire path of the share to mount the filesystem.
- Mount the filesystem
- Create a mount point directory somewhere in your host (
/cephfs, is used here)
mkdir /cephfs
- You can use the ceph driver to permanently mount your CephFS device by adding the following in the VM fstab
:/volumes/_nogroup/f6cb8f06-f0a4-4b88-b261-f8bd6b03582c /cephfs/ ceph name=MyCephFS-RW 0 2
:/volumes/_nogroup/f6cb8f06-f0a4-4b88-b261-f8bd6b03582c /cephfs/ ceph name=MyCephFS-RW,mds_namespace=cephfs_4_2,x-systemd.device-timeout=30,x-systemd.mount-timeout=30,noatime,_netdev,rw 0 2
Notice the non-standard : before the device path. It is not a typo!
The mount options are different on different systems.
The namespace option is required for SD4H/Juno, while other options are performance tweaks.
You can also do the mount directly from the command line:
sudo mount -t ceph :/volumes/_nogroup/f6cb8f06-f0a4-4b88-b261-f8bd6b03582c /cephfs/ -o name=MyCephFS-RW
sudo mount -t ceph :/volumes/_nogroup/f6cb8f06-f0a4-4b88-b261-f8bd6b03582c /cephfs/ -o name=MyCephFS-RW,mds_namespace=cephfs_4_2,x-systemd.device-timeout=30,x-systemd.mount-timeout=30,noatime,_netdev,rw
CephFS is can also be mounted directly in user space via ceph-fuse.
Install the ceph-fuse lib
sudo dnf install ceph-fuse
Let the fuse mount be accessible in userspace by uncommenting user_allow_other in the fuse.conf file.
# mount_max = 1000
user_allow_other
You can now mount cephFS in a user’s home:
mkdir ~/my_cephfs
ceph-fuse my_cephfs/ --id=MyCephFS-RW --conf=~/ceph.conf --keyring=~/ceph.keyring --client-mountpoint=/volumes/_nogroup/f6cb8f06-f0a4-4b88-b261-f8bd6b03582c
Note that the client name is here the --id. The ceph.conf and ceph.keyring content are exactly the same as for the ceph kernel mount.
Notes
A particular share can have more than one user key provisioned for it. This allows a more granular access to the filesystem, for example, if you needed some hosts to only access the filesystem in a read-only capacity. If you have multiple keys for a share, you can add the extra keys to your host and modify the above mounting procedure. This service is not available to hosts outside of the OpenStack cluster.