Translations:Cloud Quick Start/13/fr: Difference between revisions
From Alliance Doc
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| [[File:Manage-Floating-IP-Associations-Form.png|400px|thumb| Gérer les Associations d'IP flottantes]] | | [[File:Manage-Floating-IP-Associations-Form.png|400px|thumb| Gérer les associations d'IP flottantes]] |
Revision as of 20:42, 6 April 2016
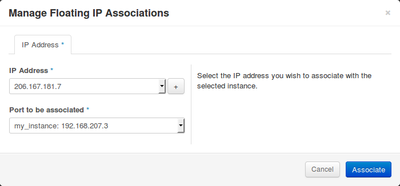
Gérer les associations d'IP flottantes
