VASP: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(Marked this version for translation) |
||
| (75 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<translate> | <translate> | ||
<!--T:1--> | <!--T:1--> | ||
: | :<i>The Vienna ab initio Simulation Package (VASP) is a computer program for atomic scale materials modelling, e.g. electronic structure calculations and quantum mechanical molecular dynamics, from first principles.</i> | ||
: Reference: [https://www.vasp.at/ VASP website] | : Reference: [https://www.vasp.at/ VASP website] | ||
== Licensing == <!--T:2--> | == Licensing == <!--T:2--> | ||
VASP is commercial software which can only be licensed to groups that are hired by a single legal entity, which is incompatible with the way we operate. We have tried to negotiate an agreement with the licensor which would let us install the software everywhere on our infrastructure, but without success. For that reason you may have to install VASP yourself (though see <i>Site exceptions</i> below). Please read the terms of your own license, as you are likely subject to the same restriction. This limits the support we are allowed to offer to users who need help installing the software. Please see [[#Building VASP yourself|<i>Building VASP yourself</i>]] below for instructions on installing the software. | |||
=== Site exceptions === <!--T:37--> | |||
Simon Fraser University, the University of Waterloo, and the University of Toronto own [[Cedar]], [[Graham]], and [[Niagara]], respectively, and have a license with VASP. Some of their employees are therefore allowed to access and install specific versions of VASP on those clusters and provide limited support. | |||
<!--T:3--> | <!--T:3--> | ||
If you wish to use the | If you wish to use the prebuilt VASP binaries on [[Cedar]], [[Graham]] and/or [[Niagara]], you must contact [[Technical support]] requesting access to VASP with the following information: | ||
* Include | * Include license holder (your PI) information: | ||
* | ** Name | ||
** Email address | |||
** Department and institution (university) | |||
* Include license information: | |||
** Version of the VASP license (<b>VASP version 4 or version 5</b>) | |||
** <b>License number</b> | |||
** Provide an updated list of who is allowed to use your VASP license. For example, forward to us the most recent email from the VASP license administrator that contains the list of licensed users. | |||
<!--T:4--> | <!--T:4--> | ||
If you are licensed for version 5 you may also use version 4, but a version 4 license does not permit you to use version 5. | If you are licensed for version 5 you may also use version 4, but a version 4 license does not permit you to use version 5. The same for version 6, if you are licensed for version 6 you may also use versions 5 and 4. | ||
== Using | == Using prebuilt VASP == <!--T:6--> | ||
<!--T:29--> | |||
Prebuilt VASP binary files have been installed only on Cedar, Graham, and Niagara. According to our license agreement, we are not allowed to install VASP centrally on other computer clusters. However, users may want to install VASP on their own home directory. Please have a look at [[VASP#Building VASP yourself|<i>Building VASP yourself</i>]]. To load prebuilt VASP on Graham and Cedar, please do the following: | |||
<!--T:7--> | <!--T:7--> | ||
Run <code>module spider vasp</code> to see | # Run <code>module spider vasp</code> to see which versions are available. | ||
# Choose your version and run <code>module spider vasp/<version></code> to see which dependencies you need to load for this particular version. | |||
# Load the dependencies and the VASP module, for example: | |||
module load intel/2020.1.217 intelmpi/2019.7.217 vasp/5.4.4 | |||
See [[Using modules]] for more information. | |||
<!--T:41--> | |||
To use VASP on Niagara, please see [https://docs.scinet.utoronto.ca/index.php/VASP the SciNet VASP wiki page]. Note that Niagara nodes do not have GPUs, so GPU versions are not available on that system. | |||
=== Pseudopotential files === <!--T:8--> | === Pseudopotential files === <!--T:8--> | ||
All pseudopotentials have been downloaded from the official VASP website and untarred. They are all located in <code> $EBROOTVASP | All pseudopotentials have been downloaded from the official VASP website and untarred. They are all located in <code> $EBROOTVASP/pseudopotentials/</code> on Cedar and Graham and can be accessed once the VASP module is loaded. | ||
=== Executable programs === <!--T:9--> | === Executable programs === <!--T:9--> | ||
<!--T:10--> | <!--T:10--> | ||
For VASP-4.6, | <b>For VASP-4.6</b>, executable files are: | ||
* <code>vasp</code> for standard NVT calculations with non | * <code>vasp</code> for standard NVT calculations with non gamma k points | ||
* <code>vasp-gamma</code> | * <code>vasp-gamma</code> for standard NVT calculations with only gamma points | ||
* <code>makeparam</code> | * <code>makeparam</code> to estimate how much memory is required to run VASP for a particular cluster | ||
<!--T:22--> | <!--T:22--> | ||
For VASP-5.4.1, | <b>For VASP-5.4.1, 5.4.4 and 6.1.0 (without CUDA support)</b>, executable files are: | ||
* <code>vasp_std</code> for standard NVT | * <code>vasp_std</code> for standard NVT calculations with non gamma k points | ||
* <code>vasp_gam</code> for standard NVT | * <code>vasp_gam</code> for standard NVT calculations with only gamma points | ||
* <code>vasp_ncl</code> for NPT | * <code>vasp_ncl</code> for NPT calculations with non gamma k points | ||
<!--T:24--> | |||
<b>For VASP-5.4.4 and 6.1.0 (with CUDA support)</b>, executable files are: | |||
* <code>vasp_gpu</code> for standard NVT calculations with gamma and non gamma k points | |||
* <code>vasp_gpu_ncl</code> for NPT calculations with gamma and non gamma k points | |||
<!--T:23--> | <!--T:23--> | ||
| Line 45: | Line 71: | ||
If you need a version of VASP that does not appear here, you can either build it yourself (see below) or [[Technical support | write to us]] and ask that it be built and installed. | If you need a version of VASP that does not appear here, you can either build it yourself (see below) or [[Technical support | write to us]] and ask that it be built and installed. | ||
== | == Vasp-GPU == <!--T:25--> | ||
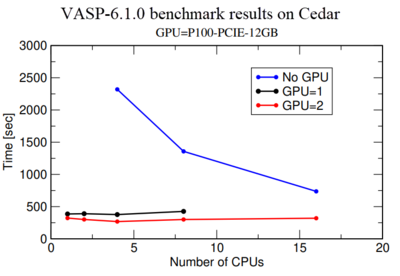
[[File:VASP benchmark ENG.png|400px|thumb| Fig.1 Simulation time as a function of the number of CPUs for GPU=0, 1, and 2]] | |||
Vasp-GPU executable files run on both GPUs and CPUs of a node. Basically, calculation on a GPU is much more expensive than on a CPU, therefore we highly recommend to perform a benchmark using one or 2 GPUs to make sure they are getting a maximum performance from the GPU use. Fig.1 shows a benchmark of Si crystal which contains 256 Si-atoms in the simulation box. Blue, black and red lines show simulation time as a function of Number of CPU for GPU=0, 1, and 2 respectively. It shows the performance for GPU=1,2 and CPU=1 is more than 5 times better compared to GPU=0 and CPU=1. However, a comparison of calculations with GPU=1 and GPU=2 indicates that there is not much performance gain from GPU=1 to GPU=2. In fact, use for GPU=2 is around 50% in our monitoring system. Therefore we recommend users to first perform a benchmark like this for their own system to make sure they are not wasting any computer resources. | |||
== Example of a VASP job script == <!--T:15--> | == Example of a VASP job script == <!--T:15--> | ||
| Line 65: | Line 90: | ||
#SBATCH --mem-per-cpu=1024M # memory | #SBATCH --mem-per-cpu=1024M # memory | ||
#SBATCH --time=0-00:05 # time (DD-HH:MM) | #SBATCH --time=0-00:05 # time (DD-HH:MM) | ||
module load vasp/<VERSION> | module load intel/2020.1.217 intelmpi/2019.7.217 vasp/<VERSION> | ||
srun <VASP> | srun <VASP> | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 71: | Line 96: | ||
<!--T:18--> | <!--T:18--> | ||
*The above job script requests four CPU cores and 4096MB memory (4x1024MB). | *The above job script requests four CPU cores and 4096MB memory (4x1024MB). | ||
*<ACCOUNT> is a Slurm account name; see [[Running_jobs#Accounts_and_projects|Accounts and projects]] | *<ACCOUNT> is a Slurm account name; see [[Running_jobs#Accounts_and_projects|Accounts and projects]] to know what to enter there. | ||
*<VERSION> is the VASP version | *<VERSION> is the number for the VASP version you want to use: 4.6, 5.4.1, 5.4.4 or 6.1.0. | ||
*<VASP> is the name of the executable. | *Use module spider vasp/<VERSION> to see how you can change this particular version. | ||
*<VASP> is the name of the executable. Refer to section ''Executable programs'' above for the executables you can select for each version. | |||
<!--T:27--> | |||
{{File | |||
|name=vasp_gpu_job.sh | |||
|lang="sh" | |||
|contents= | |||
#!/bin/bash | |||
#SBATCH --account=<ACCOUNT> | |||
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1 # number of CPU processes | |||
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:p100:1 # Number of GPU type:p100 (valid type only for cedar) | |||
#SBATCH --mem=3GB # memory | |||
#SBATCH --time=0-00:05 # time (DD-HH:MM) | |||
module load intel/2020.1.217 cuda/11.0 openmpi/4.0.3 vasp/<VERSION> | |||
srun <VASP> | |||
}} | |||
<!--T:28--> | |||
*The above job script requests one CPU core and 1024MB memory. | |||
*The above job script requests one GPU type p100 which is only available on Cedar. For other clusters, please see the [[Using GPUs with Slurm#Available_hardware|GPU types available]]. | |||
*The above job uses <code>srun</code> to run VASP. | |||
<!--T:19--> | <!--T:19--> | ||
VASP uses four input files named as | VASP uses four input files named as INCAR, KPOINTS, POSCAR, POTCAR. It is best to prepare VASP input files in a separate directory for each job. To submit the job from that directory, use: | ||
sbatch vasp_job.sh | sbatch vasp_job.sh | ||
<!--T:20--> | <!--T:20--> | ||
If you do not know how much memory you need for your job, prepare all your input files and then run <code>makeparam</code> in an interactive job submission. Then use the result as required memory for the next run. | If you do not know how much memory you need for your job, prepare all your input files and then run <code>makeparam</code> in an [[Running_jobs#Interactive_jobs|interactive job submission]]. Then use the result as required memory for the next run. However, for a more accurate estimate for future jobs, check the maximum stack size used by [[Running_jobs#Completed_jobs|completed jobs]] and use this as the memory requirement per processor for the next job. | ||
<!--T:21--> | <!--T:21--> | ||
If you want to use 32 or more cores, please read about [[Job_scheduling_policies#Whole_nodes_versus_cores|whole-node scheduling]]. | If you want to use 32 or more cores, please read about [[Job_scheduling_policies#Whole_nodes_versus_cores|whole-node scheduling]]. | ||
== Building VASP yourself == <!--T:12--> | |||
<!--T:31--> | |||
If you are licensed to use VASP and have access to VASP source code, you can install VASP-5.4.4, 6.1.2, 6.2.1 and 6.3.0 in your /home directory on all our clusters (except Niagara) using one of the following [[EasyBuild]] commands. The VASP build will be the same as the ones on Cedar and Graham, and will include the Transition State Tools and VASPsol extensions. | |||
<!--T:42--> | |||
For 2020 environment, <code> StdEnv/2020 </code> | |||
<!--T:32--> | |||
<code> eb -f VASP-5.4.4-iimpi-2020a.eb --sourcepath=SOURCEPATH </code> | |||
<!--T:33--> | |||
<code> eb -f VASP-6.1.2-iimpi-2020a.eb --sourcepath=SOURCEPATH </code> | |||
<!--T:34--> | |||
<code> eb -f VASP-6.2.1-iimpi-2020a.eb --sourcepath=SOURCEPATH </code> | |||
<!--T:35--> | |||
<code> eb -f VASP-6.3.0-iimpi-2020a.eb --sourcepath=SOURCEPATH </code> | |||
<!--T:43--> | |||
For 2023 environment, <code> StdEnv/2023 </code> | |||
<!--T:44--> | |||
<code> eb -f VASP-5.4.4-iofb-2023a.eb --sourcepath=SOURCEPATH </code> | |||
<!--T:45--> | |||
<code> eb -f VASP-6.4.2-iofb-2023a.eb --sourcepath=SOURCEPATH </code> | |||
<!--T:38--> | |||
where SOURCEPATH is the path to the VASP source file. The source files for vasp-5.4.4, 6.1.2, 6.2.1, and 6.3.0 are <code> vasp.5.4.4.pl2.tgz </code>, <code> vasp.6.1.2_patched.tgz </code>, <code> vasp.6.2.1.tgz </code> and <code> vasp.6.3.0.tgz </code> respectively. You may download the source code from the [https://www.vasp.at/ VASP website]. Running the command will take some time, perhaps more than an hour. Once it is done, you will be able to load and run VASP using <code>module</code> commands just as explained above in [[VASP#Using_prebuilt_VASP|Using prebuilt VASP]]. | |||
<!--T:14--> | <!--T:14--> | ||
[[Category:Software]] | Alternatively to build a custom version of VASP, please see [[Installing software in your home directory]] and | ||
[https://www.vasp.at/wiki/index.php/Installing_VASP.5.X.X Installing VASP 5] or [https://www.vasp.at/wiki/index.php/Installing_VASP.6.X.X Installing VASP 6]. | |||
= External links = <!--T:39--> | |||
<!--T:40--> | |||
* [https://www.vasp.at/tutorials/latest/part1/ Getting Started] guide from the developers' Web site. | |||
* [https://www.vasp.at/py4vasp/latest/ py4vasp] is a Python interface to extract data from VASP calculations. | |||
<!--T:36--> | |||
[[Category:Software]][[Category:ComputationalChemistry]] | |||
</translate> | </translate> | ||
Latest revision as of 21:32, 30 April 2024
- The Vienna ab initio Simulation Package (VASP) is a computer program for atomic scale materials modelling, e.g. electronic structure calculations and quantum mechanical molecular dynamics, from first principles.
- Reference: VASP website
Licensing[edit]
VASP is commercial software which can only be licensed to groups that are hired by a single legal entity, which is incompatible with the way we operate. We have tried to negotiate an agreement with the licensor which would let us install the software everywhere on our infrastructure, but without success. For that reason you may have to install VASP yourself (though see Site exceptions below). Please read the terms of your own license, as you are likely subject to the same restriction. This limits the support we are allowed to offer to users who need help installing the software. Please see Building VASP yourself below for instructions on installing the software.
Site exceptions[edit]
Simon Fraser University, the University of Waterloo, and the University of Toronto own Cedar, Graham, and Niagara, respectively, and have a license with VASP. Some of their employees are therefore allowed to access and install specific versions of VASP on those clusters and provide limited support.
If you wish to use the prebuilt VASP binaries on Cedar, Graham and/or Niagara, you must contact Technical support requesting access to VASP with the following information:
- Include license holder (your PI) information:
- Name
- Email address
- Department and institution (university)
- Include license information:
- Version of the VASP license (VASP version 4 or version 5)
- License number
- Provide an updated list of who is allowed to use your VASP license. For example, forward to us the most recent email from the VASP license administrator that contains the list of licensed users.
If you are licensed for version 5 you may also use version 4, but a version 4 license does not permit you to use version 5. The same for version 6, if you are licensed for version 6 you may also use versions 5 and 4.
Using prebuilt VASP[edit]
Prebuilt VASP binary files have been installed only on Cedar, Graham, and Niagara. According to our license agreement, we are not allowed to install VASP centrally on other computer clusters. However, users may want to install VASP on their own home directory. Please have a look at Building VASP yourself. To load prebuilt VASP on Graham and Cedar, please do the following:
- Run
module spider vaspto see which versions are available. - Choose your version and run
module spider vasp/<version>to see which dependencies you need to load for this particular version. - Load the dependencies and the VASP module, for example:
module load intel/2020.1.217 intelmpi/2019.7.217 vasp/5.4.4
See Using modules for more information.
To use VASP on Niagara, please see the SciNet VASP wiki page. Note that Niagara nodes do not have GPUs, so GPU versions are not available on that system.
Pseudopotential files[edit]
All pseudopotentials have been downloaded from the official VASP website and untarred. They are all located in $EBROOTVASP/pseudopotentials/ on Cedar and Graham and can be accessed once the VASP module is loaded.
Executable programs[edit]
For VASP-4.6, executable files are:
vaspfor standard NVT calculations with non gamma k pointsvasp-gammafor standard NVT calculations with only gamma pointsmakeparamto estimate how much memory is required to run VASP for a particular cluster
For VASP-5.4.1, 5.4.4 and 6.1.0 (without CUDA support), executable files are:
vasp_stdfor standard NVT calculations with non gamma k pointsvasp_gamfor standard NVT calculations with only gamma pointsvasp_nclfor NPT calculations with non gamma k points
For VASP-5.4.4 and 6.1.0 (with CUDA support), executable files are:
vasp_gpufor standard NVT calculations with gamma and non gamma k pointsvasp_gpu_nclfor NPT calculations with gamma and non gamma k points
Two extensions have also been incorporated:
If you need a version of VASP that does not appear here, you can either build it yourself (see below) or write to us and ask that it be built and installed.
Vasp-GPU[edit]
Vasp-GPU executable files run on both GPUs and CPUs of a node. Basically, calculation on a GPU is much more expensive than on a CPU, therefore we highly recommend to perform a benchmark using one or 2 GPUs to make sure they are getting a maximum performance from the GPU use. Fig.1 shows a benchmark of Si crystal which contains 256 Si-atoms in the simulation box. Blue, black and red lines show simulation time as a function of Number of CPU for GPU=0, 1, and 2 respectively. It shows the performance for GPU=1,2 and CPU=1 is more than 5 times better compared to GPU=0 and CPU=1. However, a comparison of calculations with GPU=1 and GPU=2 indicates that there is not much performance gain from GPU=1 to GPU=2. In fact, use for GPU=2 is around 50% in our monitoring system. Therefore we recommend users to first perform a benchmark like this for their own system to make sure they are not wasting any computer resources.
Example of a VASP job script[edit]
The following is a job script to run VASP in parallel using the Slurm job scheduler:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --account=<ACCOUNT>
#SBATCH --ntasks=4 # number of MPI processes
#SBATCH --mem-per-cpu=1024M # memory
#SBATCH --time=0-00:05 # time (DD-HH:MM)
module load intel/2020.1.217 intelmpi/2019.7.217 vasp/<VERSION>
srun <VASP>
- The above job script requests four CPU cores and 4096MB memory (4x1024MB).
- <ACCOUNT> is a Slurm account name; see Accounts and projects to know what to enter there.
- <VERSION> is the number for the VASP version you want to use: 4.6, 5.4.1, 5.4.4 or 6.1.0.
- Use module spider vasp/<VERSION> to see how you can change this particular version.
- <VASP> is the name of the executable. Refer to section Executable programs above for the executables you can select for each version.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --account=<ACCOUNT>
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1 # number of CPU processes
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:p100:1 # Number of GPU type:p100 (valid type only for cedar)
#SBATCH --mem=3GB # memory
#SBATCH --time=0-00:05 # time (DD-HH:MM)
module load intel/2020.1.217 cuda/11.0 openmpi/4.0.3 vasp/<VERSION>
srun <VASP>
- The above job script requests one CPU core and 1024MB memory.
- The above job script requests one GPU type p100 which is only available on Cedar. For other clusters, please see the GPU types available.
- The above job uses
srunto run VASP.
VASP uses four input files named as INCAR, KPOINTS, POSCAR, POTCAR. It is best to prepare VASP input files in a separate directory for each job. To submit the job from that directory, use:
sbatch vasp_job.sh
If you do not know how much memory you need for your job, prepare all your input files and then run makeparam in an interactive job submission. Then use the result as required memory for the next run. However, for a more accurate estimate for future jobs, check the maximum stack size used by completed jobs and use this as the memory requirement per processor for the next job.
If you want to use 32 or more cores, please read about whole-node scheduling.
Building VASP yourself[edit]
If you are licensed to use VASP and have access to VASP source code, you can install VASP-5.4.4, 6.1.2, 6.2.1 and 6.3.0 in your /home directory on all our clusters (except Niagara) using one of the following EasyBuild commands. The VASP build will be the same as the ones on Cedar and Graham, and will include the Transition State Tools and VASPsol extensions.
For 2020 environment, StdEnv/2020
eb -f VASP-5.4.4-iimpi-2020a.eb --sourcepath=SOURCEPATH
eb -f VASP-6.1.2-iimpi-2020a.eb --sourcepath=SOURCEPATH
eb -f VASP-6.2.1-iimpi-2020a.eb --sourcepath=SOURCEPATH
eb -f VASP-6.3.0-iimpi-2020a.eb --sourcepath=SOURCEPATH
For 2023 environment, StdEnv/2023
eb -f VASP-5.4.4-iofb-2023a.eb --sourcepath=SOURCEPATH
eb -f VASP-6.4.2-iofb-2023a.eb --sourcepath=SOURCEPATH
where SOURCEPATH is the path to the VASP source file. The source files for vasp-5.4.4, 6.1.2, 6.2.1, and 6.3.0 are vasp.5.4.4.pl2.tgz , vasp.6.1.2_patched.tgz , vasp.6.2.1.tgz and vasp.6.3.0.tgz respectively. You may download the source code from the VASP website. Running the command will take some time, perhaps more than an hour. Once it is done, you will be able to load and run VASP using module commands just as explained above in Using prebuilt VASP.
Alternatively to build a custom version of VASP, please see Installing software in your home directory and Installing VASP 5 or Installing VASP 6.
External links[edit]
- Getting Started guide from the developers' Web site.
- py4vasp is a Python interface to extract data from VASP calculations.